Page 1419 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1419
992 PART 8: Renal and Metabolic Disorders
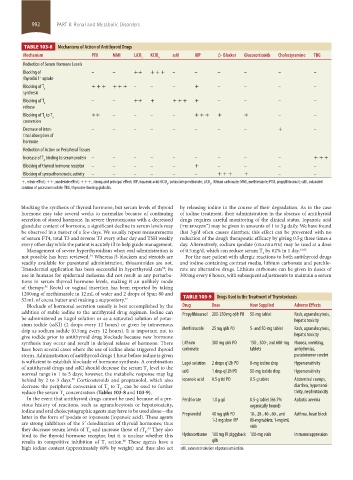
TABLE 103-8 Mechanisms of Action of Antithyroid Drugs
Mechanism PTU MMI LiCO KClO ssKI IOP β- Blocker Glucocorticoids Cholestyramine TBG
3 4
Reduction of Serum Hormone Levels
Blocking of – – ++ + + + – – – – – –
−
thyroidal I uptake
Blocking of T 4 + + + + + + – – – + – – – –
synthesis
Blocking of T 4 – – ++ + + + + + – – – –
release
Blocking of T to T 3 ++ – – – – + + + + + – –
4
conversion
Decrease of intes- – – – – – – – – + –
tinal absorption of
hormone
Reduction of Action on Peripheral Tissues
Increase of T binding to serum protein – – – – – – – – – + + +
4
Blocking of thyroid hormone receptor – – – – – + – – – –
Blocking of sympathomimetic activity – – – – – – + + + + – –
+, minor effect; ++, moderate effect; +++, strong and principal effect; IOP, iopanoic acid; KClO , potassium perchlorate; LiCO , lithium carbonate; MMI, methimazole; PTU, propylthiouracil; ssKI, saturated
4
3
solution of potassium iodide; TBG, thyroxine-binding globulin.
blocking the synthesis of thyroid hormone, but serum levels of thyroid by releasing iodine in the course of their degradation. As in the case
hormone may take several weeks to normalize because of continuing of iodine treatment, their administration in the absence of antithyroid
secretion of stored hormone. In severe thyrotoxicosis with a decreased drugs requires careful monitoring of the clinical status. Iopanoic acid
glandular content of hormone, a significant decline in serum levels may (telepaque™) may be given in amounts of 1 to 3 g daily. We have found
be observed in a matter of a few days. We usually repeat measurements that 3 g/d often causes diarrhea; this effect can be prevented with no
of serum FT4, total T3 and reverse T3 every other day and TSH weekly reduction of the drug’s therapeutic efficacy by giving 0.5 g three times a
every other day while the patient is acutely ill to help guide management. day. Alternatively, sodium ipodate (oragrafin) may be used at a dose
Management of severe hyperthyroidism when oral administration is of 0.5 mg/d, which can reduce serum T by 62% in 1 day. 61,62
3
not possible has been reviewed. Whereas β-blockers and steroids are For the rare patient with allergic reactions to both antithyroid drugs
54
readily available for parenteral administration, thioaminides are not. and iodine-containing contrast media, lithium carbonate and perchlo-
Transdermal application has been successful in hyperthyroid cats ; its rate are alternative drugs. Lithium carbonate can be given in doses of
55
use in humans for epidermal melasma did not result in any perturba- 300 mg every 6 hours, with subsequent adjustments to maintain a serum
tions in serum thyroid hormone levels, making it an unlikely mode
of therapy. Rectal or vaginal insertion has been reported by taking
56
1200 mg of methimazole in 12 mL of water and 2 drops of Span 80 and
52 mL of cocoa butter and making a suppository. 57 TABLE 103-9 Drugs Used in the Treatment of Thyrotoxicosis
Blockade of hormonal secretion usually is best accomplished by the Drug Dose How Supplied Adverse Effects
addition of stable iodine to the antithyroid drug regimen. Iodine can Propylthiouracil 200-250 mg q6h PO 50-mg tablet Rash, agranulocytosis,
be administered as Lugol solution or as a saturated solution of potas- hepatic toxicity
sium iodide (ssKI) (2 drops every 12 hours) or given by intravenous
drip as sodium iodide (0.5 mg every 12 hours). It is important not to Methimazole 25 mg q6h PO 5- and 50-mg tablet Rash, agranulocytosis,
give iodide prior to antithyroid drug blockade because new hormone hepatic toxicity
synthesis may occur and result in delayed release of hormone. There Lithium 300 mg q6h PO 150-, 300-, and 600-mg Nausea, vomiting,
have been several cases where the use of iodine alone triggered thyroid carbonate tablets arrhythmias,
storm. Administration of antithyroid drugs 1 hour before iodine is given pseudotumor cerebri
is sufficient to establish blockade of hormone synthesis. A combination Lugol solution 2 drops q12h PO 8-mg iodine drop Hypersensitivity
of antithyroid drugs and ssKI should decrease the serum T level to the
3
normal range in 1 to 5 days; however, the metabolic response may lag ssKI 1 drop q12h PO 50-mg iodide drop Hypersensitivity
behind by 2 to 3 days. Corticosteroids and propranolol, which also Iopanoic acid 0.5 g tid PO 0.5-g tablet Abdominal cramps,
58
decrease the peripheral conversion of T to T , can be used to further diarrhea, hypersensi-
3
4
reduce the serum T concentration (Tables 103-8 and 103-9). tivity, nephrotoxicity
3
In the event that antithyroid drugs cannot be used because of a pre- Perchlorate 1.0 g qd 0.5-g tablet (66.7% Aplastic anemia
vious history of reactions, such as agranulocytosis or hepatotoxicity, organically bound)
iodine and oral cholecystographic agents may have to be used alone—the
latter in the form of ipodate or iopanoate (iopanoic acid). These agents Propranolol 40 mg q6h PO 10-, 20-, 40-, 60-, and Asthma, heart block
are strong inhibitors of the 5′ deiodination of thyroid hormones; thus 1-3 mg slow IVP 80-mg tablets; 1-mg/mL
they decrease serum levels of T and increase those of rT . They also vials
59
3
3
bind to the thyroid hormone receptor, but it is unclear whether this Hydrocortisone 100 mg IV piggyback 100-mg vials Immunosuppression
results in competitive inhibition of T action. These agents have a q8h
60
3
high iodine content (approximately 60% by weight) and thus also act ssKI, saturated solution of potassium iodide.
section08.indd 992 1/14/2015 8:28:37 AM