Page 1494 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1494
CHAPTER 108: Acute Pancreatitis 1033
The clinical course after an episode of acute pancreatitis is quite vari-
TABLE 108-2 Revised Atlanta Classification (2012) for Pancreatic and
Peripancreatic Fluid Collections able and it is of utmost importance to detect high-risk patients who
will progress to severe, necrotizing pancreatitis in an effort to improve
Definition Duration CECT (Contrast-Enhanced CT) Features outcomes. Multiple clinical scoring systems have been used to pre-
Acute fluid collection (AFC) <4 weeks • Homogenous with fluid density dict the severity of acute pancreatitis. These scoring systems are very
• No encapsulation important because they can help recognize patients with severe acute
• Interstitial edematous pancreatitis pancreatitis who would require aggressive care in the intensive care
unit. Ranson criteria have been shown to be moderately accurate in
Acute necrotic collection (ANC) <4 weeks • Heterogenous (both fluid and solid predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis, 17-19 but it takes 48 hours after
components) initial hospitalization to be calculated and involves laboratory values
• No encapsulation that are not routinely checked. As such, it is not frequently used. The
• Acute necrotizing pancreatitis
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Examination II (APACHE II)
Pseudocyst (PP) >4 weeks • Homogenous with fluid density score was initially developed for critically ill patients and is currently the
• Well defined wall most widely used scoring system for severity of acute pancreatitis. It is as
• After interstitial edematous pancreatitis accurate as the Ranson criteria and is faster to calculate. Recently, a new
20
Walled-off necrosis (WON) >4 weeks • Heterogenous (both fluid and solid scoring method known as bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis
21
components (BISAP) was developed in an attempt to recognize early disease severity.
• Well defined wall It is based on blood urea nitrogen (BUN) >25 mg/dL, impaired mental
• After acute necrotizing pancreatitis status, presence of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), age
>60 years, and presence of pleural effusions. Even though it is simpler
and quick to calculate, it has been found to have lower sensitivity than
both Ranson and APACHE II scores in predicting severity, pancreatic
necrosis, and mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. 22
The revised Atlanta classification has attempted to simplify this classi-
fication of severity of acute pancreatitis and it divides acute pancreatitis
into mild acute pancreatitis, moderately severe acute pancreatitis, and
severe acute pancreatitis. This classification is based on the presence or
4
absence of organ failure and local or systemic complications. In the clas-
sification, transient organ failure refers to organ failure that is present for
<48 hours, while persistent organ failure is present for >48 hours after
Liver onset. Local complications refer to acute peripancreatic fluid collections
or pancreatic necrosis. Exacerbation of previously present comorbidi-
ties is considered systemic complication. The modified Marshall scor-
Spleen ing system is used for assessing organ failure. It involves assessment of
cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal systems.
Mild acute pancreatitis is associated with very low mortality and
is characterized by the absence of organ failure, local and systemic
complications. Most of these patients do not require cross-sectional
imaging and have a short hospital stay. Moderately severe pancreatitis is
characterized by presence of transient organ failure or local or systemic
complications but persistent organ failure is absent; mortality rate is also
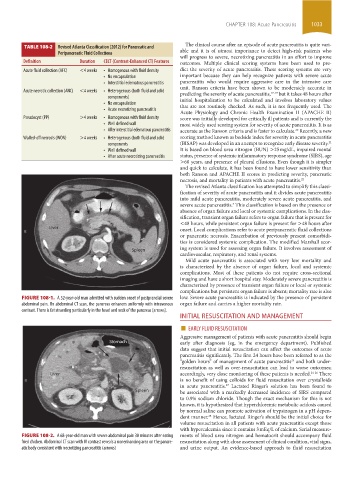
FIGURE 108-1. A 52-year-old man admitted with sudden onset of postprandial severe low. Severe acute pancreatitis is indicated by the presence of persistent
abdominal pain. On abdominal CT scan, the pancreas enhances uniformly with intravenous organ failure and carries a higher mortality rate.
contrast. There is fat stranding particularly in the head and neck of the pancreas (arrows).
INITIAL RESUSCITATION AND MANAGEMENT
■ EARLY FLUID RESUSCITATION
Aggressive management of patients with acute pancreatitis should begin
Stomach early after diagnosis (eg, in the emergency department). Published
data suggest that initial resuscitation can affect the outcomes of acute
pancreatitis significantly. The first 24 hours have been referred to as the
“golden hours” of management of acute pancreatitis and both under-
23
resuscitation as well as over-resuscitation can lead to worse outcomes;
Liver accordingly, very close monitoring of these patients is needed. 24-26 There
is no benefit of using colloids for fluid resuscitation over crystalloids
in acute pancreatitis. Lactated Ringer’s solution has been found to
27
Spleen be associated with a markedly decreased incidence of SIRS compared
to 0.9% sodium chloride. Though the exact mechanism for this is not
known, it is hypothesized that hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis caused
by normal saline can promote activation of trypsinogen in a pH depen-
dent manner. Hence, lactated Ringer’s should be the initial choice for
28
volume resuscitation in all patients with acute pancreatitis except those
with hypercalcemia since it contains 3 mEq/L of calcium. Serial measure-
FIGURE 108-2. A 68-year-old man with severe abdominal pain 30 minutes after eating ments of blood urea nitrogen and hematocrit should accompany fluid
fried chicken. Abdominal CT scan with IV contrast reveals a nonenhancing area on the pancre- resuscitation along with close assessment of clinical condition, vital signs,
atic body consistent with necrotizing pancreatitis (arrows) and urine output. An evidence-based approach to fluid resuscitation
section09.indd 1033 1/14/2015 9:27:21 AM