Page 1767 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1767
1236 PART 11: Special Problems in Critical Care
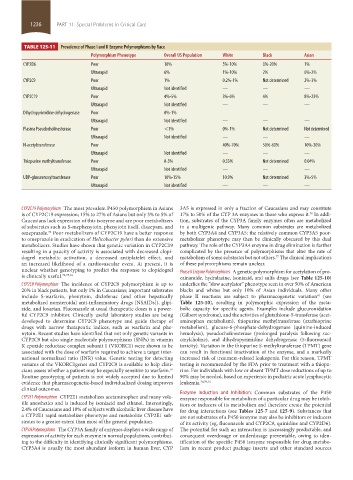
TABLE 125-11 Prevalence of Phase I and II Enzyme Polymorphisms by Race
Polymorphism Phenotype Overall US Population White Black Asian
CYP2D6 Poor 10% 5%-10% 0%-20% 1%
Ultrarapid 6% 1%-10% 2% 0%-2%
CYP2C9 Poor 1% 0.2%-1% Not determined 2%-3%
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
CYP2C19 Poor 4%-5% 3%-6% 4% 8%-23%
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase Poor 0%-1%
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
Plasma Pseudocholinesterase Poor <1% 0%-1% Not determined Not determined
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
N-acetyltransferase Poor 40%-70% 50%-60% 10%-20%
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
Thiopurine methyltransferase Poor 0-3% 0.33% Not determined 0.04%
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase Poor 10%-15% 10.9% Not determined 3%-5%
Ultrarapid Not identified — — —
CYP2C19 Polymorphism The most prevalent P450 polymorphism in Asians 3A5 is expressed in only a fraction of Caucasians and may constitute
is of CYP2C19 expression; 15% to 27% of Asians but only 3% to 5% of 17% to 50% of the CYP 3A enzymes in those who express it. In addi-
76
Caucasians lack expression of this isozyme and are poor metabolizers tion, substrates of the CYP3A family enzymes often are metabolized
of substrates such as S-mephenytoin, phenytoin itself, diazepam, and in a multigenic pathway. Many common substrates are metabolized
omeprazole. Poor metabolizers of CYP2C19 have a better response by both CYP3A4 and CYP3A5; the relatively common CYP3A5 poor-
72
to omeprazole in eradication of Helicobacter pylori than do extensive metabolizer phenotype may then be clinically obscured by this dual
metabolizers. Studies have shown that genetic variation in CYP2C19 pathway. The role of the CYP3A4 enzyme in drug elimination is further
resulting in a paucity of activity is associated with decreased clopi- complicated by the presence of polymorphisms that alter the rate of
77
dogrel metabolic activation, a decreased antiplatelet effect, and metabolism of some substrates but not others. The clinical implications
an increased likelihood of a cardiovascular event. At present, it is of these polymorphisms remain unclear.
unclear whether genotyping to predict the response to clopidogrel Phase II Enzyme Polymorphisms A genetic polymorphism for acetylation of pro-
is clinically useful. 74,75,16 cainamide, hydralazine, isoniazid, and sulfa drugs (see Table 125-10)
CYP2C9 Polymorphism The incidence of CYP2C9 polymorphism is up to underlies the “slow acetylator” phenotype seen in over 50% of American
20% in black patients, but only 1% in Caucasians; important substrates blacks and whites but only 10% of Asian individuals. Many other
61
include S-warfarin, phenytoin, diclofenac (and other hepatically phase II reactions are subject to pharmacogenetic variation (see
metabolized nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]), glipi- Table 125-10), resulting in polymorphic expression of the meta-
zide, and losartan. Fluconazole at usual therapeutic doses is a power- bolic capacity for specific agents. Examples include glucuronidation
ful CYP2C9 inhibitor. Clinically useful laboratory studies are being (Gilbert syndrome), and the activities of glutathione-S-transferase (acet-
developed to determine CYP2C9 phenotype and guide therapy of aminophen metabolism), thiopurine methyltransferase (azathioprine
drugs with narrow therapeutic indices, such as warfarin and phe- metabolism), glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (quinine-induced
nytoin. Recent studies have identified that not only genetic variants in hemolysis), pseudocholinesterase (prolonged paralysis following suc-
CYP2C9 but also single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in vitamin cinylcholine), and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (5-fluorouracil
K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1) were shown to be toxicity). Variation in the thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) gene
associated with the dose of warfarin required to achieve a target inter- can result in functional inactivation of the enzyme, and a markedly
national normalized ratio (INR) value. Genetic testing for detecting increased risk of treatment-related leukopenia. For this reason, TPMT
variants of the VKORC1genes and CYP2C9 is available to help clini- testing is recommended by the FDA prior to treatment with a thiopu-
cians assess whether a patient may be especially sensitive to warfarin. rine. For individuals with low or absent TPMT dose reductions of up to
16
Routine genotyping of patients is not widely accepted due to limited 90% may be needed, based on experience in pediatric acute lymphocytic
evidence that pharmacogenetic-based individualized dosing improves leukemia. 78,79,16
clinical outcomes. Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Common substrates of the P450
CYP2E1 Polymorphism CYP2E1 metabolizes acetaminophen and many vola- enzyme responsible for metabolism of a particular drug may be inhib-
tile anesthetics and is induced by isoniazid and ethanol. Interestingly, itors or inducers of its metabolism and therefore create the potential
2.4% of Caucasians and 10% of subjects with alcoholic liver disease have for drug interactions (see Tables 125-7 and 125-9). Substances that
a CYP2E1 rapid metabolizer phenotype and metabolize CYP2E1 sub- are not substrates of a P450 isozyme may also be inhibitors or inducers
strates to a greater extent than most of the general population. of its activity (eg, fluconazole and CYP2C9, quinidine and CYP2D6).
CYP3A Polymorphism The CYP3A family of enzymes displays a wide range of The potential for such an interaction is increasingly predictable, and
expression of activity for each enzyme in normal populations, contribut- consequent overdosage or underdosage preventable, owing to iden-
ing to the difficulty in identifying clinically significant polymorphisms. tification of the specific P450 isozyme responsible for drug metabo-
CYP3A4 is usually the most abundant isoform in human liver, CYP lism in recent product package inserts and other standard sources
section11.indd 1236 1/19/2015 10:52:12 AM