Page 609 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 609
CHAPTER 29 ■ Body Fluid Analysis 593
BOX 29.1
Clinical Correlations (Pleural Fluid)
TRANSUDATES
Congestive heart ailure
Cirrhosis with ascites
EXUDATES
In ectious diseases
Empyema
uberculosis
Malignant neoplasms
Lymphoma
Mesothelioma
Pancreatitis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Laboratory Analysis
Physical Characteristics
ransudates are usually clear, are pale yellow, and do not
clot. In comparison, exudates can display a range o colors
depending on the associated disorder ( able 29.6). Only
2 mL o circulating blood in 1 L o pleural f uid will pro-
duce a blood-tinged appearance. Very viscous f uids, clear
or bloody, are characteristic o mesothelioma. In addition,
exudates may be cloudy or purulent and requently clot on
standing because o the presence o brinogen.
Specimen turbidity may be caused by lipids or result rom
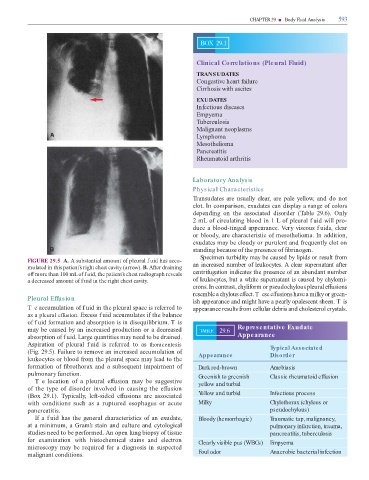
FIGURE 29.5 A. A substantial amount o pleural f uid has accu-
mulated in this patient’s right chest cavity (arrow). B. A er draining an increased number o leukocytes. A clear supernatant a er
o more than 100 mL o f uid, the patient’s chest radiograph reveals centri ugation indicates the presence o an abundant number
a decreased amount o f uid in the right chest cavity. o leukocytes, but a white supernatant is caused by chylomi-
crons. In contrast, chyli orm or pseudochylous pleural e usions
resemble a chylous e ect. T ese e usions have a milky or green-
Pleural Effusion
ish appearance and might have a pearly opalescent sheen. T is
T e accumulation o f uid in the pleural space is re erred to appearance results rom cellular debris and cholesterol crystals.
as a pleural effusion. Excess f uid accumulates i the balance
o f uid ormation and absorption is in disequilibrium. T is
may be caused by an increased production or a decreased TABLE 29.6 Representative Exudate
absorption o f uid. Large quantities may need to be drained. Appearance
Aspiration o pleural f uid is re erred to as thoracentesis Typical Associated
(Fig. 29.5). Failure to remove an increased accumulation o Appearance Disorder
leukocytes or blood rom the pleural space may lead to the
ormation o brothorax and a subsequent impairment o Dark red-brown Amebiasis
pulmonary unction. Greenish to greenish Classic rheumatoid effusion
Te location o a pleural e usion may be suggestive yellow and turbid
o the type o disorder involved in causing the e usion
(Box 29.1). ypically, le -sided e usions are associated Yellow and turbid Infectious process
with conditions such as a ruptured esophagus or acute Milky Chylothorax (chylous or
pancreatitis. pseudochylous)
I a f uid has the general characteristics o an exudate, Bloody (hemorrhagic) Traumatic tap, malignancy,
at a minimum, a Gram’s stain and culture and cytological pulmonary infarction, trauma,
studies need to be per ormed. An open lung biopsy o tissue pancreatitis, tuberculosis
or examination with histochemical stains and electron Clearly visible pus (WBCs) Empyema
microscopy may be required or a diagnosis in suspected
malignant conditions. Foul odor Anaerobic bacterial infection