Page 611 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 611
CHAPTER 29 ■ Body Fluid Analysis 595
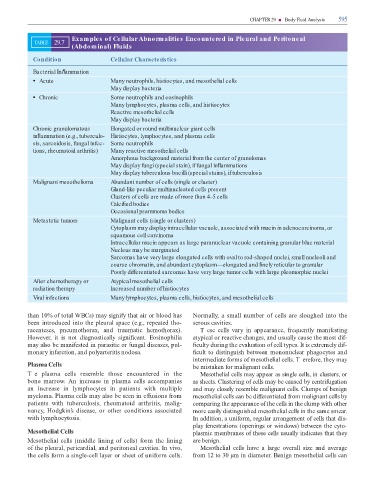
Examples of Cellular Abnormalities Encountered in Pleural and Peritoneal
TABLE 29.7
(Abdominal) Fluids
Condition Cellular Characteristics
Bacterial In ammation
Acute Many neutrophils, histiocytes, and mesothelial cells
May display bacteria
Chronic Some neutrophils and eosinophils
Many lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histiocytes
Reactive mesothelial cells
May display bacteria
Chronic granulomatous Elongated or round multinuclear giant cells
in ammation (e.g., tuberculo- Histiocytes, lymphocytes, and plasma cells
sis, sarcoidosis, fungal infec- Some neutrophils
tions, rheumatoid arthritis) Many reactive mesothelial cells
Amorphous background material from the center of granulomas
May display fungi (special stain), if fungal in ammations
May display tuberculous bacilli (special stains), if tuberculosis
Malignant mesothelioma Abundant number of cells (single or cluster)
Gland-like peculiar multinucleated cells present
Clusters of cells are made of more than 4–5 cells
Calci ed bodies
Occasional psammoma bodies
Metastatic tumors Malignant cells (single or clusters)
Cytoplasm may display intracellular vacuole, associated with mucin in adenocarcinoma, or
squamous cell carcinoma
Intracellular mucin appears as large paranuclear vacuole containing granular blue material
Nucleus may be marginated
Sarcomas have very large elongated cells with oval to rod-shaped nuclei, small nucleoli and
coarse chromatin, and abundant cytoplasm—elongated and nely reticular to granular
Poorly differentiated sarcomas have very large tumor cells with large pleomorphic nuclei
After chemotherapy or Atypical mesothelial cells
radiation therapy Increased number of histiocytes
Viral infections Many lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes, and mesothelial cells
than 10% o total WBCs) may signi y that air or blood has Normally, a small number o cells are sloughed into the
been introduced into the pleural space (e.g., repeated tho- serous cavities.
racenteses, pneumothorax, and traumatic hemothorax). T ese cells vary in appearance, requently mani esting
However, it is not diagnostically signi cant. Eosinophilia atypical or reactive changes, and usually cause the most di -
may also be mani ested in parasitic or ungal diseases, pul- culty during the evaluation o cell types. It is extremely di -
monary in arction, and polyarteritis nodosa. cult to distinguish between mononuclear phagocytes and
intermediate orms o mesothelial cells. T ere ore, they may
Plasma Cells be mistaken or malignant cells.
Te plasma cells resemble those encountered in the Mesothelial cells may appear as single cells, in clusters, or
bone marrow. An increase in plasma cells accompanies as sheets. Clustering o cells may be caused by centri ugation
an increase in lymphocytes in patients with multiple and may closely resemble malignant cells. Clumps o benign
myeloma. Plasma cells may also be seen in e usions rom mesothelial cells can be di erentiated rom malignant cells by
patients with tuberculosis, rheumatoid arthritis, malig- comparing the appearance o the cells in the clump with other
nancy, Hodgkin’s disease, or other conditions associated more easily distinguished mesothelial cells in the same smear.
with lymphocytosis. In addition, a uni orm, regular arrangement o cells that dis-
play enestrations (openings or windows) between the cyto-
Mesothelial Cells plasmic membranes o these cells usually indicates that they
Mesothelial cells (middle lining o cells) orm the lining are benign.
o the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal cavities. In vivo, Mesothelial cells have a large overall size and average
the cells orm a single-cell layer or sheet o uni orm cells. rom 12 to 30 µm in diameter. Benign mesothelial cells can