Page 698 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 698
682 PART 8 ■ Fundamentals of Hematological Analysis
SPECIAL HEMATOLOGY PROCEDURES (continued)
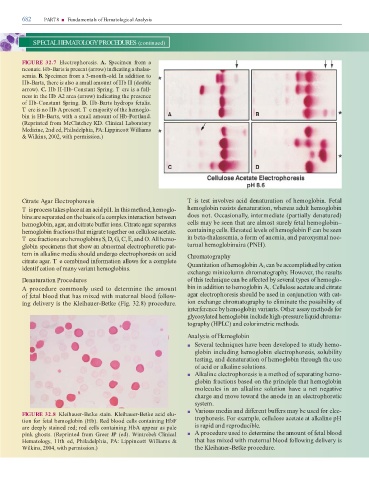
FIGURE 32.7 Electrophoresis. A. Specimen rom a
neonate. Hb-Barts is present (arrow) in icating a thalas-
semia. B. Specimen rom a 3-month-ol . In a ition to
Hb-Barts, there is also a small amount o Hb H (double
arrow). C. Hb H-Hb-Constant Spring. T ere is a ull-
ness in the Hb A2 area (arrow) in icating the presence
o Hb-Constant Spring. D. Hb-Barts hy rops etalis.
T ere is no Hb A present. T e majority o the hemoglo-
bin is Hb-Barts, with a small amount o Hb-Portlan .
(Reprinte rom McClatchey KD. Clinical Laboratory
Medicine, 2n e , Phila elphia, PA: Lippincott Williams
& Wilkins, 2002, with permission.)
Citrate Agar Electrophoresis Tis test involves aci enaturation o hemoglobin. Fetal
T is process takes place at an aci pH. In this metho , hemoglo- hemoglobin resists enaturation, whereas a ult hemoglobin
bins are separate on the basis o a complex interaction between oes not. Occasionally, interme iate (partially enature )
hemoglobin, agar, an citrate bu er ions. Citrate agar separates cells may be seen that are almost surely etal hemoglobin–
hemoglobin ractions that migrate together on cellulose acetate. containing cells. Elevate levels o hemoglobin F can be seen
Tese ractions are hemoglobins S, D, G, C, E, an O. All hemo- in beta-thalassemia, a orm o anemia, an paroxysmal noc-
globin specimens that show an abnormal electrophoretic pat- turnal hemoglobinuira (PNH).
tern in alkaline me ia shoul un ergo electrophoresis on aci Chromatography
citrate agar. T e combine in ormation allows or a complete Quantitation o hemoglobin A can be accomplishe by cation
i entif cation o many variant hemoglobins. 1
exchange minicolumn chromatography. However, the results
Denaturation Procedures o this technique can be a ecte by several types o hemoglo-
A proce ure commonly use to etermine the amount bin in a ition to hemoglobin A . Cellulose acetate an citrate
1
o etal bloo that has mixe with maternal bloo ollow- agar electrophoresis shoul be use in conjunction with cat-
ing elivery is the Kleihauer-Betke (Fig. 32.8) proce ure. ion exchange chromatography to eliminate the possibility o
inter erence by hemoglobin variants. Other assay metho s or
glycosylate hemoglobin inclu e high-pressure liqui chroma-
tography (HPLC) an colorimetric metho s.
Analysis of Hemoglobin
■ Several techniques have been evelope to stu y hemo-
globin inclu ing hemoglobin electrophoresis, solubility
testing, an enaturation o hemoglobin through the use
o aci or alkaline solutions.
■ Alkaline electrophoresis is a metho o separating hemo-
globin ractions base on the principle that hemoglobin
molecules in an alkaline solution have a net negative
charge an move towar the ano e in an electrophoretic
system.
FIGURE 32.8 Kleihauer-Betke stain. Kleihauer-Betke aci elu- ■ Various me ia an i erent bu ers may be use or elec-
tion or etal hemoglobin (Hb). Re bloo cells containing HbF trophoresis. For example, cellulose acetate at alkaline pH
are eeply staine re ; re cells containing HbA appear as pale is rapi an repro ucible.
pink ghosts. (Reprinte rom Greer JP (e ). Wintrobe’s Clinical ■ A proce ure use to etermine the amount o etal bloo
Hematology, 11th e , Phila elphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & that has mixe with maternal bloo ollowing elivery is
Wilkins, 2004, with permission.) the Kleihauer-Betke proce ure.