Page 165 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 165
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
154
PART II Clinical Bacteriology
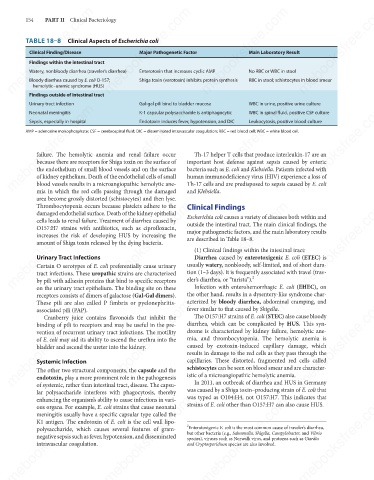
TABLE 18–8 Clinical Aspects of Escherichia coli
Major Pathogenetic Factor
Clinical Finding/Disease
Main Laboratory Result
Findings within the intestinal tract
Enterotoxin that increases cyclic AMP
Watery, nonbloody diarrhea (traveler’s diarrhea)
No RBC or WBC in stool
Bloody diarrhea caused by E. coli O-157;
Shiga toxin (verotoxin) inhibits protein synthesis
RBC in stool; schistocytes in blood smear
hemolytic–uremic syndrome (HUS)
Findings outside of intestinal tract
WBC in urine, positive urine culture
Urinary tract infection
Gal-gal pili bind to bladder mucosa
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com and Klebsiella. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Neonatal meningitis
WBC in spinal fluid, positive CSF culture
K-1 capsular polysaccharide is antiphagocytic
Endotoxin induces fever, hypotension, and DIC
Sepsis, especially in hospital
Leukocytosis, positive blood culture
AMP = adenosine monophosphate; CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation; RBC = red blood cell; WBC = white blood cell.
Th-17 helper T cells that produce interleukin-17 are an
failure. The hemolytic anemia and renal failure occur
important host defense against sepsis caused by enteric
because there are receptors for Shiga toxin on the surface of
the endothelium of small blood vessels and on the surface
bacteria such as E. coli and Klebsiella. Patients infected with
of kidney epithelium. Death of the endothelial cells of small
Th-17 cells and are predisposed to sepsis caused by E. coli
blood vessels results in a microangiopathic hemolytic ane-
mia in which the red cells passing through the damaged
area become grossly distorted (schistocytes) and then lyse. human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) experience a loss of
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com outside the intestinal tract. The main clinical findings, the mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Thrombocytopenia occurs because platelets adhere to the
Clinical Findings
damaged endothelial surface. Death of the kidney epithelial
Escherichia coli causes a variety of diseases both within and
cells leads to renal failure. Treatment of diarrhea caused by
O157:H7 strains with antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin,
major pathogenetic factors, and the main laboratory results
increases the risk of developing HUS by increasing the
are described in Table 18–8.
amount of Shiga toxin released by the dying bacteria.
(1) Clinical findings within the intestinal tract:
Urinary Tract Infections
Diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) is
usually watery, nonbloody, self-limited, and of short dura-
Certain O serotypes of E. coli preferentially cause urinary
tract infections. These uropathic strains are characterized
2
eler’s diarrhea, or “turista”).
by pili with adhesin proteins that bind to specific receptors
Infection with enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC), on
on the urinary tract epithelium. The binding site on these
the other hand, results in a dysentery-like syndrome char-
receptors consists of dimers of galactose (Gal-Gal dimers). tion (1–3 days). It is frequently associated with travel (trav-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com diarrhea, which can be complicated by HUS. This syn- mebooksfree.com
acterized by bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and
mebooksfree.com
These pili are also called P fimbria or pyelonephritis-
fever similar to that caused by Shigella.
associated pili (PAP).
The O157:H7 strains of E. coli (STEC) also cause bloody
Cranberry juice contains flavonoids that inhibit the
binding of pili to receptors and may be useful in the pre-
drome is characterized by kidney failure, hemolytic ane-
vention of recurrent urinary tract infections. The motility
mia, and thrombocytopenia. The hemolytic anemia is
of E. coli may aid its ability to ascend the urethra into the
caused by exotoxin-induced capillary damage, which
bladder and ascend the ureter into the kidney.
results in damage to the red cells as they pass through the
capillaries. These distorted, fragmented red cells called
Systemic Infection
schistocytes can be seen on blood smear and are character-
The other two structural components, the capsule and the
endotoxin, play a more prominent role in the pathogenesis
In 2011, an outbreak of diarrhea and HUS in Germany
of systemic, rather than intestinal tract, disease. The capsu-
was caused by a Shiga toxin–producing strain of E. coli that
lar polysaccharide interferes with phagocytosis, thereby istic of a microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.
was typed as O104:H4, not O157:H7. This indicates that
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 2 but other bacteria (e.g., Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, and Vibrio mebooksfree.com
enhancing the organism’s ability to cause infections in vari-
strains of E. coli other than O157:H7 can also cause HUS.
ous organs. For example, E. coli strains that cause neonatal
meningitis usually have a specific capsular type called the
K1 antigen. The endotoxin of E. coli is the cell wall lipo-
Enterotoxigenic E. coli is the most common cause of traveler’s diarrhea,
polysaccharide, which causes several features of gram-
negative sepsis such as fever, hypotension, and disseminated
species), viruses such as Norwalk virus, and protozoa such as Giardia
intravascular coagulation.
and Cryptosporidium species are also involved.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com