Page 300 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 300
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 1 mebooksfree.com Recurrent Infection Route of Transmission 289 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 37 DNA Enveloped Viruses
TABLE 37–1 Important Features of Common Herpesvirus Infections
Virus
Primary Infection
Usual Site of Latency
2,3
Cranial sensory ganglia
HSV-1
Via respiratory secretions and
Gingivostomatitis
Herpes labialis, encephalitis,
keratitis
saliva
HSV-2
Lumbar or sacral sensory
Herpes genitalis, perinatal
disseminated disease
ganglia
2
Zoster
Via respiratory secretions
Varicella
VZV
Cranial or thoracic sensory
ganglia Herpes genitalis 2,3 3,4 Sexual contact, perinatal infection
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 6 mebooksfree.com Kaposi’s sarcoma Sexual or organ transplantation mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
1
B lymphocytes
Infectious mononucleosis
Asymptomatic shedding
EBV
Via respiratory secretions and
saliva
2
CMV
Asymptomatic shedding
Intrauterine infection, transfusions,
Monocytes
Congenital infection (in
1
sexual contact, via secretions
utero), mononucleosis
(e.g., saliva and urine)
5
HHV-8
Uncertain
Uncertain
CMV = cytomegalovirus; EBV = Epstein–Barr virus; HHV-8 = human herpesvirus 8; HSV = herpes simplex virus; VZV = varicella-zoster virus.
1
Primary infection is often asymptomatic.
2
In immunocompromised patients, dissemination of virus can cause life-threatening disease.
3
Asymptomatic shedding also occurs.
4
Latent EBV infection predisposes to B-cell lymphomas.
5
Also known as Kaposi’s sarcoma–associated herpesvirus.
6
A mononucleosis-like syndrome has been described. Kaposi’s sarcoma itself also can result from a primary infection.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com HSV types 1 and 2 and VZV, infect epithelial cells primarily mebooksfree.com
Some information is available regarding the mechanism
by which herpes simplex virus (HSV) and cytomegalovirus
and cause latent infection in neurons. The beta herpesvi-
(CMV) initiate and maintain the latent state. Shortly after
ruses, consisting of CMVs and human herpesvirus 6, infect
HSV infects neurons, a set of “latency-associated tran-
and become latent in a variety of tissues. The gamma her-
pesviruses, consisting of EBV and human herpesvirus 8
scripts” (LATS) are synthesized. These noncoding, regula-
(HHV-8, Kaposi’s sarcoma–associated virus), infect and
tory RNAs suppress viral replication. The precise
mechanism by which they do so is unknown. The process
become latent primarily in lymphoid cells. Table 37–2
by which latency is terminated and reactivation of viral
replication occurs is unclear, but various triggers such as
herpesviruses.
Certain herpesviruses are associated with or cause can-
sunlight, fever, and stress are known. CMV establishes
latency by producing microRNAs that inhibit the transla- describes some important clinical features of the common
cer in humans (e.g., Epstein–Barr virus is associated with
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
tion of mRNAs required for viral replication. Also, the
CMV genome encodes a protein and an RNA that have the
ability to inhibit apoptosis in infected cells. Inhibition of
apoptosis allows the infected cell to survive.
Three of the herpesviruses, HSV types 1 and 2 and var-
icella-zoster virus (VZV), cause a vesicular rash, both in
primary infections and in reactivations. Primary infections
are usually more severe than reactivations. The other two
herpesviruses, CMV and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), do not
cause a vesicular rash.
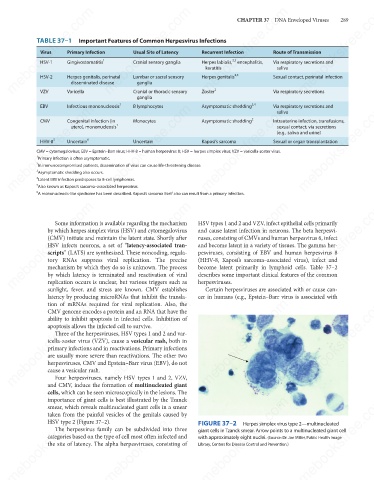
Four herpesviruses, namely HSV types 1 and 2, VZV,
and CMV, induce the formation of multinucleated giant
cells, which can be seen microscopically in the lesions. The
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 37–2 Herpes simplex virus type 2—multinucleated mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
importance of giant cells is best illustrated by the Tzanck
smear, which reveals multinucleated giant cells in a smear
taken from the painful vesicles of the genitals caused by
HSV type 2 (Figure 37–2).
The herpesvirus family can be subdivided into three
giant cells in Tzanck smear. Arrow points to a multinucleated giant cell
categories based on the type of cell most often infected and
with approximately eight nuclei. (Source: Dr. Joe Miller, Public Health Image
the site of latency. The alpha herpesviruses, consisting of
Library, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com