Page 377 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 377
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com that codes for a protein that binds to DNA. The conclusion mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART IV Clinical Virology
366
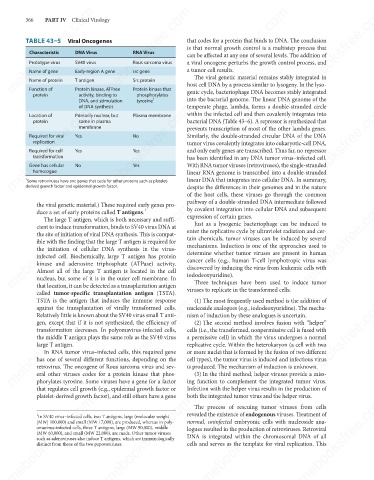
TABLE 43–5 Viral Oncogenes
is that normal growth control is a multistep process that
DNA Virus
RNA Virus
Characteristic
can be affected at any one of several levels. The addition of
a viral oncogene perturbs the growth control process, and
Rous sarcoma virus
Prototype virus
SV40 virus
a tumor cell results.
Name of gene
src gene
Early-region A gene
The viral genetic material remains stably integrated in
T antigen
Name of protein
Protein kinase that
Protein kinase, ATPase
Function of
genic cycle, bacteriophage DNA becomes stably integrated
protein
activity, binding to
phosphorylates
into the bacterial genome. The linear DNA genome of the
DNA, and stimulation Src protein 1 host cell DNA by a process similar to lysogeny. In the lyso-
tyrosine
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com prevents transcription of most of the other lambda genes. mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
temperate phage, lambda, forms a double-stranded circle
of DNA synthesis
within the infected cell and then covalently integrates into
Plasma membrane
Location of
Primarily nuclear, but
bacterial DNA (Table 43–6). A repressor is synthesized that
some in plasma
protein
membrane
Similarly, the double-stranded circular DNA of the DNA
No
Yes
Required for viral
replication
tumor virus covalently integrates into eukaryotic-cell DNA,
and only early genes are transcribed. Thus far, no repressor
Required for cell
Yes
Yes
transformation
has been identified in any DNA tumor virus–infected cell.
With RNA tumor viruses (retroviruses), the single-stranded
No
Yes
Gene has cellular
homologue
linear RNA genome is transcribed into a double-stranded
linear DNA that integrates into cellular DNA. In summary,
1
Some retroviruses have onc genes that code for other proteins such as platelet-
despite the differences in their genomes and in the nature
derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor.
of the host cells, these viruses go through the common
pathway of a double-stranded DNA intermediate followed
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com enter the replicative cycle by ultraviolet radiation and cer- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
the viral genetic material.) These required early genes pro-
by covalent integration into cellular DNA and subsequent
1
duce a set of early proteins called T antigens.
expression of certain genes.
The large T antigen, which is both necessary and suffi-
Just as a lysogenic bacteriophage can be induced to
cient to induce transformation, binds to SV40 virus DNA at
the site of initiation of viral DNA synthesis. This is compat-
tain chemicals, tumor viruses can be induced by several
ible with the finding that the large T antigen is required for
mechanisms. Induction is one of the approaches used to
the initiation of cellular DNA synthesis in the virus-
determine whether tumor viruses are present in human
infected cell. Biochemically, large T antigen has protein
cancer cells (e.g., human T-cell lymphotropic virus was
kinase and adenosine triphosphate (ATPase) activity.
discovered by inducing the virus from leukemic cells with
Almost all of the large T antigen is located in the cell
nucleus, but some of it is in the outer cell membrane. In
Three techniques have been used to induce tumor
that location, it can be detected as a transplantation antigen
viruses to replicate in the transformed cells:
called tumor-specific transplantation antigen (TSTA). iododeoxyuridine).
TSTA is the antigen that induces the immune response
(1) The most frequently used method is the addition of
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com cells (i.e., the transformed, nonpermissive cell is fused with mebooksfree.com
against the transplantation of virally transformed cells.
nucleoside analogues (e.g., iododeoxyuridine). The mecha-
Relatively little is known about the SV40 virus small T anti-
nism of induction by these analogues is uncertain.
gen, except that if it is not synthesized, the efficiency of
(2) The second method involves fusion with “helper”
transformation decreases. In polyomavirus-infected cells,
the middle T antigen plays the same role as the SV40 virus
a permissive cell) in which the virus undergoes a normal
large T antigen.
replicative cycle. Within the heterokaryon (a cell with two
In RNA tumor virus–infected cells, this required gene
or more nuclei that is formed by the fusion of two different
has one of several different functions, depending on the
cell types), the tumor virus is induced and infectious virus
retrovirus. The oncogene of Rous sarcoma virus and sev-
is produced. The mechanism of induction is unknown.
eral other viruses codes for a protein kinase that phos-
(3) In the third method, helper viruses provide a miss-
phorylates tyrosine. Some viruses have a gene for a factor
ing function to complement the integrated tumor virus.
Infection with the helper virus results in the production of
that regulates cell growth (e.g., epidermal growth factor or
platelet-derived growth factor), and still others have a gene
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com both the integrated tumor virus and the helper virus. mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
The process of rescuing tumor viruses from cells
revealed the existence of endogenous viruses. Treatment of
1
In SV40 virus–infected cells, two T antigens, large (molecular weight
normal, uninfected embryonic cells with nucleoside ana-
[MW] 100,000) and small (MW 17,000), are produced, whereas in poly-
omavirus-infected cells, three T antigens, large (MW 90,000), middle
logues resulted in the production of retroviruses. Retroviral
(MW 60,000), and small (MW 22,000), are made. Other tumor viruses
DNA is integrated within the chromosomal DNA of all
such as adenoviruses also induce T antigens, which are immunologically
cells and serves as the template for viral replication. This
distinct from those of the two papovaviruses.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com