Page 434 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 434
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART VI PARASITOLOGY
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com egg to larva to adult. The egg contains an embryo that, mebooksfree.com
Many helminths have a life cycle that progresses from
Parasites occur in two distinct forms: single-celled proto-
zoa and multicellular metazoa called helminths or worms.
For medical purposes, protozoa can be subdivided into
matures into the adult form that produces the eggs.
four groups: Sarcodina (amebas), Sporozoa (sporozoans),
Mastigophora (flagellates), and Ciliata (ciliates). Metazoa
There are special terms applied to the host of certain
parasites as they proceed through their life cycle. A defini-
are subdivided into two phyla: the Platyhelminthes (flat- upon hatching, differentiates into a larval form, which then
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com examination of the stool for ova and parasites (O&P) is mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
tive host is one in which the sexual cycle occurs or the
worms) and the Nemathelminthes (roundworms, nema-
todes). The phylum Platyhelminthes contains two medically
adult is present, and the intermediate host is one in which
important classes: Cestoda (tapeworms) and Trematoda
the asexual cycle occurs or the larva is present.
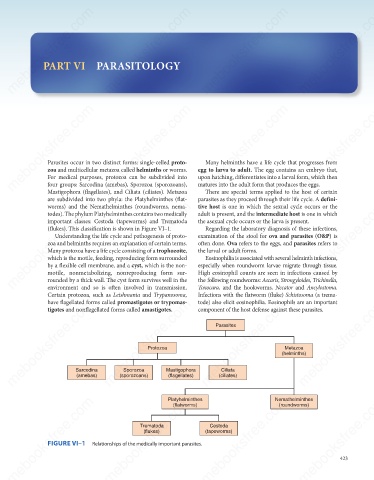
(flukes). This classification is shown in Figure VI–1.
Regarding the laboratory diagnosis of these infections,
Understanding the life cycle and pathogenesis of proto-
zoa and helminths requires an explanation of certain terms.
often done. Ova refers to the eggs, and parasites refers to
the larval or adult forms.
Many protozoa have a life cycle consisting of a trophozoite,
which is the motile, feeding, reproducing form surrounded
Eosinophilia is associated with several helminth infections,
especially when roundworm larvae migrate through tissue.
by a flexible cell membrane, and a cyst, which is the non-
motile, nonmetabolizing, nonreproducing form sur-
rounded by a thick wall. The cyst form survives well in the
the following roundworms: Ascaris, Strongyloides, Trichinella,
Toxocara, and the hookworms, Necator and Ancylostoma.
environment and so is often involved in transmission.
Infections with the flatworm (fluke) Schistosoma (a trema-
Certain protozoa, such as Leishmania and Trypanosoma, High eosinophil counts are seen in infections caused by
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (helminths) mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
have flagellated forms called promastigotes or trypomas-
tode) also elicit eosinophilia. Eosinophils are an important
component of the host defense against these parasites.
tigotes and nonflagellated forms called amastigotes.
Parasites
o
a
z
M
a t e
o
a
o t o r P
z
Sarcodina
Sporozoa
Ciliata
Mastigophora
(ciliates)
(amebas)
(sporozoans)
(flagellates)
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Relationships of the medically important parasites. (tapeworms) Nemathelminthes 423 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Platyhelminthes
(flatworms)
(roundworms)
Cestoda
Trematoda
(flukes)
FIGURE VI–1
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com