Page 501 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 501
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
PART VII Immunology
490
T cells
B cells
Cytokines (IL-4, IL-5)
Helper (CD4)
Cytotoxic (CD8)
cells
cells
Plasma cells
IL-2
IL-2
Activated cytotoxic cells
Activated
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com toxins and viruses Inhibit intracellular virus-infected cells mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Kill bacteria mebooksfree.com
helper cells and
macrophages
Antibodies
+
Kill
Neutralize
bacteria and fungi
Complement
+
Neutrophils
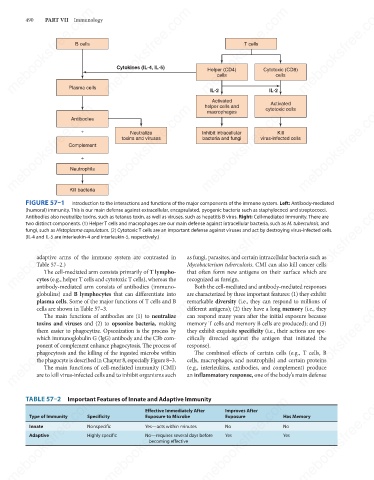
FIGURE 57–1
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com as fungi, parasites, and certain intracellular bacteria such as mebooksfree.com
Introduction to the interactions and functions of the major components of the immune system. Left: Antibody-mediated
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
(humoral) immunity. This is our main defense against extracellular, encapsulated, pyogenic bacteria such as staphylococci and streptococci.
Antibodies also neutralize toxins, such as tetanus toxin, as well as viruses, such as hepatitis B virus. Right: Cell-mediated immunity. There are
two distinct components. (1) Helper T cells and macrophages are our main defense against intracellular bacteria, such as M. tuberculosis, and
fungi, such as Histoplasma capsulatum. (2) Cytotoxic T cells are an important defense against viruses and act by destroying virus-infected cells.
(IL-4 and IL-5 are interleukin-4 and interleukin-5, respectively.)
adaptive arms of the immune system are contrasted in
Table 57–2.)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. CMI can also kill cancer cells
The cell-mediated arm consists primarily of T lympho-
cytes (e.g., helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells), whereas the
recognized as foreign.
Both the cell-mediated and antibody-mediated responses
antibody-mediated arm consists of antibodies (immuno-
are characterized by three important features: (1) they exhibit
globulins) and B lymphocytes that can differentiate into that often form new antigens on their surface which are
mebooksfree.com
remarkable diversity (i.e., they can respond to millions of
mebooksfree.com
plasma cells. Some of the major functions of T cells and B
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com memory T cells and memory B cells are produced); and (3) mebooksfree.com
different antigens); (2) they have a long memory (i.e., they
cells are shown in Table 57–3.
can respond many years after the initial exposure because
The main functions of antibodies are (1) to neutralize
toxins and viruses and (2) to opsonize bacteria, making
them easier to phagocytize. Opsonization is the process by
they exhibit exquisite specificity (i.e., their actions are spe-
cifically directed against the antigen that initiated the
which immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody and the C3b com-
response).
ponent of complement enhance phagocytosis. The process of
phagocytosis and the killing of the ingested microbe within
The combined effects of certain cells (e.g., T cells, B
the phagocyte is described in Chapter 8, especially Figure 8–3.
cells, macrophages, and neutrophils) and certain proteins
(e.g., interleukins, antibodies, and complement) produce
The main functions of cell-mediated immunity (CMI)
are to kill virus-infected cells and to inhibit organisms such
an inflammatory response, one of the body’s main defense
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Specificity mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Has Memory mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
TABLE 57–2 Important Features of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Improves After
Effective Immediately After
Exposure
Type of Immunity
Exposure to Microbe
Innate
No
Nonspecific
No
Yes—acts within minutes
Adaptive
Yes
Yes
No—requires several days before
Highly specific
becoming effective
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com