Page 503 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 503
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Virus mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART VII Immunology
492
APC (antigen-
presenting cell),
APC
e.g., macrophage
(immunogen)
or dendritic cell
Class II MHC
Antigen processing within macrophage;
protein
viral proteins cleaved into small peptides
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Viral epitope APC receptor Activation of helper T cell mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Helper
T
CD4
cell
T-cell
for Ag (TCR)
IL-2 receptor TCR Helper Activation IgM monomer
T
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Cytotoxic IL2-R IL-2 Memory TH CD4 mebooksfree.com (immunogen) mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
cell
IL-4, IL-5
IL-2
of B cell
Activation of
B cell
cytotoxic T cell
Cytotoxins
TCR
Viral
CD4
Virus
epitope
T cell
cell
TCR
Differentiation
Cell death TCR CD8 Plasma
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com CD8 mebooksfree.com Memory B mebooksfree.com Antibody mebooksfree.com
Class
I MHC
cell
Virus-
protein
infected
cell
cell
Memory Tc
cell
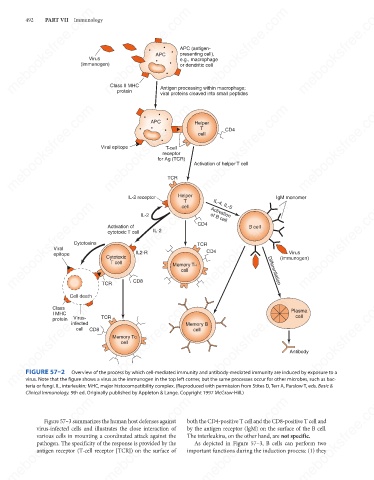
FIGURE 57–2
Overview of the process by which cell-mediated immunity and antibody-mediated immunity are induced by exposure to a
virus. Note that the figure shows a virus as the immunogen in the top left corner, but the same processes occur for other microbes, such as bac-
teria or fungi. IL, interleukin; MHC, major histocompatibility complex. (Reproduced with permission from Stites D, Terr A, Parslow T, eds. Basic &
Clinical Immunology. 9th ed. Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1997 McGraw-Hill.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com both the CD4-positive T cell and the CD8-positive T cell and mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Figure 57–3 summarizes the human host defenses against
virus-infected cells and illustrates the close interaction of
by the antigen receptor (IgM) on the surface of the B cell.
various cells in mounting a coordinated attack against the
The interleukins, on the other hand, are not specific.
pathogen. The specificity of the response is provided by the
As depicted in Figure 57–3, B cells can perform two
antigen receptor (T-cell receptor [TCR]) on the surface of
important functions during the induction process: (1) they
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com