Page 558 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 558
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
bodies are highly specific).mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com CHAPTER 64 Antigen–Antibody Reactions in the Laboratory 547 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
autoimmune diseases, and in the typing of blood and tis-
sues prior to transplantation.
Microorganisms and other cells possess a variety of
antigens and thus induce antisera containing many differ-
ent antibodies (i.e., the antisera are polyclonal). Monoclo-
nal antibodies excel in the identification of antigens because
cross-reacting antibodies are absent (i.e., monoclonal anti-
Immune precipitate formed
TYPES OF DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Many types of diagnostic tests are performed in the immu-
nology laboratory. Most of these tests can be designed to
determine the presence of either antigen or antibody. To do
this, one of the components, either antigen or antibody, is
known and the other is unknown. For example, with a known
antigen such as influenza virus, a test can determine whether
antibody to the virus is present in the patient’s serum. Alter-
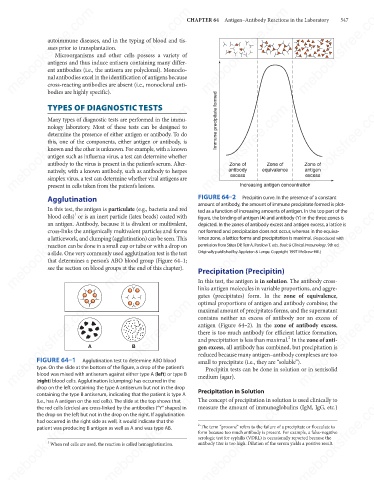
Zone of
Zone of
Zone of
antigen
antibody
equivalence
natively, with a known antibody, such as antibody to herpes
excess
excess
simplex virus, a test can determine whether viral antigens are
present in cells taken from the patient’s lesions.
Agglutination FIGURE 64–2 Increasing antigen concentration
Precipitin curve. In the presence of a constant
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com depicted. In the zones of antibody excess and antigen excess, a lattice is mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
amount of antibody, the amount of immune precipitate formed is plot-
In this test, the antigen is particulate (e.g., bacteria and red
ted as a function of increasing amounts of antigen. In the top part of the
1
blood cells) or is an inert particle (latex beads) coated with
figure, the binding of antigen (▲) and antibody (Y) in the three zones is
an antigen. Antibody, because it is divalent or multivalent,
cross-links the antigenically multivalent particles and forms
not formed and precipitation does not occur, whereas in the equiva-
a latticework, and clumping (agglutination) can be seen. This
lence zone, a lattice forms and precipitation is maximal. (Reproduced with
reaction can be done in a small cup or tube or with a drop on
permission from Stites DP, Terr A, Parslow T, eds. Basic & Clinical Immunology. 9th ed.
Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1997 McGraw-Hill.)
a slide. One very commonly used agglutination test is the test
that determines a person’s ABO blood group (Figure 64–1;
see the section on blood groups at the end of this chapter).
Precipitation (Precipitin)
In this test, the antigen is in solution. The antibody cross-
links antigen molecules in variable proportions, and aggre-
gates (precipitates) form. In the zone of equivalence,
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com A mebooksfree.com antigen (Figure 64–2). In the zone of antibody excess, mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
optimal proportions of antigen and antibody combine; the
maximal amount of precipitates forms, and the supernatant
contains neither an excess of antibody nor an excess of
there is too much antibody for efficient lattice formation,
2
and precipitation is less than maximal. In the zone of anti-
gen excess, all antibody has combined, but precipitation is
B
reduced because many antigen–antibody complexes are too
FIGURE 64–1
Agglutination test to determine ABO blood
small to precipitate (i.e., they are “soluble”).
type. On the slide at the bottom of the figure, a drop of the patient’s
Precipitin tests can be done in solution or in semisolid
blood was mixed with antiserum against either type A (left) or type B
(right) blood cells. Agglutination (clumping) has occurred in the
drop on the left containing the type A antiserum but not in the drop
Precipitation in Solution
containing the type B antiserum, indicating that the patient is type A medium (agar).
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 2 form because too much antibody is present. For example, a false-negative mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
The concept of precipitation in solution is used clinically to
(i.e., has A antigen on the red cells). The slide at the top shows that
measure the amount of immunoglobulins (IgM, IgG, etc.)
the red cells (circles) are cross-linked by the antibodies (“Y” shapes) in
the drop on the left but not in the drop on the right. If agglutination
had occurred in the right side as well, it would indicate that the
The term “prozone” refers to the failure of a precipitate or flocculate to
patient was producing B antigen as well as A and was type AB.
serologic test for syphilis (VDRL) is occasionally reported because the
1
antibody titer is too high. Dilution of the serum yields a positive result.
When red cells are used, the reaction is called hemagglutination.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com