Page 563 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 563
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com p24 Gel mebooksfree.com Paper Paper mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
552
PART VII Immunology
Paper
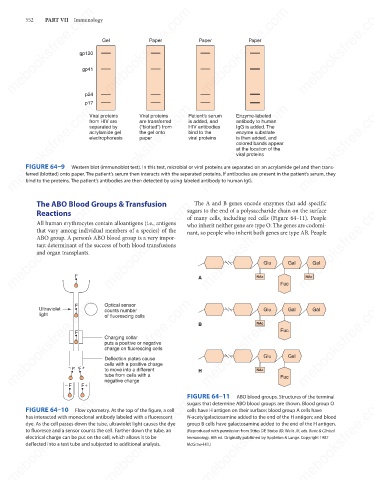
gp120
gp41
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com p17 mebooksfree.com Patient’s serum Enzyme-labeled mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Viral proteins
Viral proteins
are transferred
from HIV are
is added, and
antibody to human
HIV antibodies
IgG is added. The
separated by
(“blotted”) from
the gel onto
enzyme substrate
acrylamide gel
bind to the
is then added, and
viral proteins
electrophoresis
paper
colored bands appear
at the location of the
viral proteins
FIGURE 64–9
Western blot (immunoblot test). In this test, microbial or viral proteins are separated on an acrylamide gel and then trans-
ferred (blotted) onto paper. The patient’s serum then interacts with the separated proteins. If antibodies are present in the patient’s serum, they
bind to the proteins. The patient’s antibodies are then detected by using labeled antibody to human IgG.
The ABO Blood Groups & Transfusion
The A and B genes encode enzymes that add specific
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com sugars to the end of a polysaccharide chain on the surface mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Reactions
of many cells, including red cells (Figure 64–11). People
All human erythrocytes contain alloantigens (i.e., antigens
who inherit neither gene are type O. The genes are codomi-
that vary among individual members of a species) of the
nant, so people who inherit both genes are type AB. People
ABO group. A person’s ABO blood group is a very impor-
tant determinant of the success of both blood transfusions
and organ transplants.
Gal
Gal
Glu
F
NAc
NAc
A
Fuc
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Optical sensor B mebooksfree.com Fuc Gal mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
F
Ultraviolet
Glu
Gal
counts number
light
of fluorescing cells
NAc
F
Charging collar
puts a positive or negative
charge on fluorescing cells
Gal
Glu
Deflection plates cause
cells with a positive charge
F F +
–
to move into a different
NAc
H
tube from cells with a
Fuc
negative charge
–
F +
F
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 64–11 ABO blood groups. Structures of the terminal mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
sugars that determine ABO blood groups are shown. Blood group O
FIGURE 64–10
Flow cytometry. At the top of the figure, a cell
cells have H antigen on their surface; blood group A cells have
has interacted with monoclonal antibody labeled with a fluorescent
N-acetylgalactosamine added to the end of the H antigen; and blood
dye. As the cell passes down the tube, ultraviolet light causes the dye
group B cells have galactosamine added to the end of the H antigen.
to fluoresce and a sensor counts the cell. Farther down the tube, an
(Reproduced with permission from Stites DP, Stobo JD, Wells JV, eds. Basic & Clinical
electrical charge can be put on the cell, which allows it to be
Immunology. 6th ed. Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1987
deflected into a test tube and subjected to additional analysis.
McGraw-Hill.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com