Page 562 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 562
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com CHAPTER 64 Antigen–Antibody Reactions in the Laboratory 551 mebooksfree.com
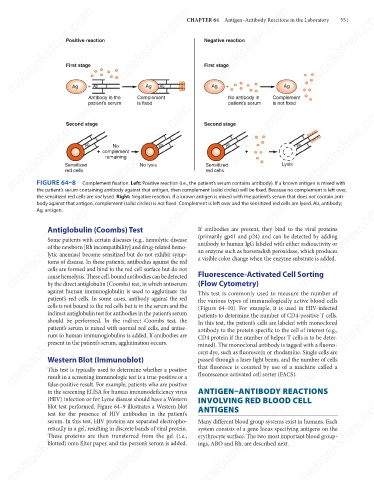
Negative reaction
Positive reaction
First stage
First stage
Ag
Ag
Ag
+
Ab
Ab
Antibody in the Complement Ag + No antibody in Complement
is not fixed
is fixed
patient’s serum
patient’s serum
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Ab + complement No lysis Ab Second stage + Lysis Ab mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Second stage
Ab
No
remaining
Sensitized
Sensitized
red cells
red cells
FIGURE 64–8
Complement fixation. Left: Positive reaction (i.e., the patient’s serum contains antibody). If a known antigen is mixed with
the patient’s serum containing antibody against that antigen, then complement (solid circles) will be fixed. Because no complement is left over,
the sensitized red cells are not lysed. Right: Negative reaction. If a known antigen is mixed with the patient’s serum that does not contain anti-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com If antibodies are present, they bind to the viral proteins mebooksfree.com
body against that antigen, complement (solid circles) is not fixed. Complement is left over and the sensitized red cells are lysed. Ab, antibody;
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Ag, antigen.
Antiglobulin (Coombs) Test
(primarily gp41 and p24) and can be detected by adding
Some patients with certain diseases (e.g., hemolytic disease
antibody to human IgG labeled with either radioactivity or
of the newborn [Rh incompatibility] and drug-related hemo-
an enzyme such as horseradish peroxidase, which produces
lytic anemias) become sensitized but do not exhibit symp-
a visible color change when the enzyme substrate is added.
toms of disease. In these patients, antibodies against the red
cells are formed and bind to the red cell surface but do not
Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting
cause hemolysis. These cell-bound antibodies can be detected
(Flow Cytometry)
by the direct antiglobulin (Coombs) test, in which antiserum
against human immunoglobulin is used to agglutinate the
This test is commonly used to measure the number of
patient’s red cells. In some cases, antibody against the red
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com the various types of immunologically active blood cells mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
cells is not bound to the red cells but is in the serum and the
(Figure 64–10). For example, it is used in HIV-infected
indirect antiglobulin test for antibodies in the patient’s serum
patients to determine the number of CD4-positive T cells.
should be performed. In the indirect Coombs test, the
In this test, the patient’s cells are labeled with monoclonal
patient’s serum is mixed with normal red cells, and antise-
antibody to the protein specific to the cell of interest (e.g.,
rum to human immunoglobulins is added. If antibodies are
CD4 protein if the number of helper T cells is to be deter-
present in the patient’s serum, agglutination occurs.
mined). The monoclonal antibody is tagged with a fluores-
cent dye, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Single cells are
Western Blot (Immunoblot)
passed through a laser light beam, and the number of cells
that fluoresce is counted by use of a machine called a
This test is typically used to determine whether a positive
result in a screening immunologic test is a true-positive or a
false-positive result. For example, patients who are positive
ANTIGEN–ANTIBODY REACTIONS
in the screening ELISA for human immunodeficiency virus fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS).
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Many different blood group systems exist in humans. Each mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
INVOLVING RED BLOOD CELL
(HIV) infection or for Lyme disease should have a Western
blot test performed. Figure 64–9 illustrates a Western blot
ANTIGENS
test for the presence of HIV antibodies in the patient’s
serum. In this test, HIV proteins are separated electropho-
retically in a gel, resulting in discrete bands of viral protein.
system consists of a gene locus specifying antigens on the
These proteins are then transferred from the gel (i.e.,
erythrocyte surface. The two most important blood group-
blotted) onto filter paper, and the person’s serum is added.
ings, ABO and Rh, are described next.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com