Page 324 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 324
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 301 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 301 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
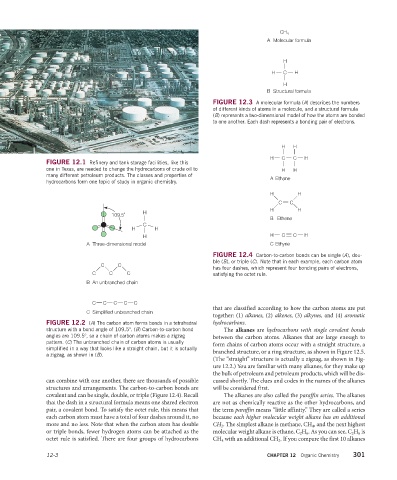
CH 4
A Molecular formula
H
H C H
H
B Structural formula
FIGURE 12.3 A molecular formula (A) describes the numbers
of different kinds of atoms in a molecule, and a structural formula
(B) represents a two-dimensional model of how the atoms are bonded
to one another. Each dash represents a bonding pair of electrons.
H H
H C C H
FIGURE 12.1 Refinery and tank storage facilities, like this
one in Texas, are needed to change the hydrocarbons of crude oil to H H
many different petroleum products. The classes and properties of
A Ethane
hydrocarbons form one topic of study in organic chemistry.
H H
C C
H H
H
109.5˚
B Ethene
C
H H
H H C C H
A Three-dimensional model C Ethyne
FIGURE 12.4 Carbon-to-carbon bonds can be single (A), dou-
ble (B), or triple (C). Note that in each example, each carbon atom
C C
has four dashes, which represent four bonding pairs of electrons,
C C C satisfying the octet rule.
B An unbranched chain
C C C C C
that are classified according to how the carbon atoms are put
C Simplified unbranched chain
together: (1) alkanes, (2) alkenes, (3) alkynes, and (4) aromatic
FIGURE 12.2 (A) The carbon atom forms bonds in a tetrahedral hydrocarbons.
structure with a bond angle of 109.5°. (B) Carbon-to-carbon bond The alkanes are hydrocarbons with single covalent bonds
angles are 109.5°, so a chain of carbon atoms makes a zigzag between the carbon atoms. Alkanes that are large enough to
pattern. (C) The unbranched chain of carbon atoms is usually form chains of carbon atoms occur with a straight structure, a
simplified in a way that looks like a straight chain, but it is actually branched structure, or a ring structure, as shown in Figure 12.5.
a zigzag, as shown in (B).
(The “straight” structure is actually a zigzag, as shown in Fig-
ure 12.2.) You are familiar with many alkanes, for they make up
the bulk of petroleum and petroleum products, which will be dis-
can combine with one another, there are thousands of possible cussed shortly. The clues and codes in the names of the alkanes
structures and arrangements. The carbon-to-carbon bonds are will be considered first.
covalent and can be single, double, or triple (Figure 12.4). Recall The alkanes are also called the paraffin series. The alkanes
that the dash in a structural formula means one shared electron are not as chemically reactive as the other hydrocarbons, and
pair, a covalent bond. To satisfy the octet rule, this means that the term paraffin means “little affinity.” They are called a series
each carbon atom must have a total of four dashes around it, no because each higher molecular weight alkane has an additional
more and no less. Note that when the carbon atom has double CH 2 . The simplest alkane is methane, CH 4 , and the next highest
or triple bonds, fewer hydrogen atoms can be attached as the molecular weight alkane is ethane, C 2 H 6 . As you can see, C 2 H 6 is
octet rule is satisfied. There are four groups of hydrocarbons CH 4 with an additional CH 2 . If you compare the first 10 alkanes
12-3 CHAPTER 12 Organic Chemistry 301