Page 327 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 327
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 304 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 304 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
Perhaps you have heard the terms saturated and unsatu- CYCLOALKANES AND AROMATIC
rated in advertisements for cooking oil and margarine. An HYDROCARBONS
organic molecule, such as a hydrocarbon, that does not contain The hydrocarbons discussed up until now have been straight
the maximum number of hydrogen atoms is an unsaturated or branched open-ended chains of carbon atoms. Carbon at-
hydrocarbon. For example, ethylene can add more hydrogen oms can also bond to one another to form a ring, or cyclic,
atoms by reacting with hydrogen gas to form ethane:
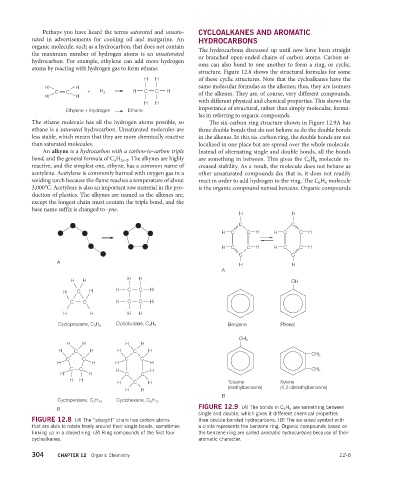
structure. Figure 12.8 shows the structural formulas for some
H H of these cyclic structures. Note that the cycloalkanes have the
H H same molecular formulas as the alkenes; thus, they are isomers
C C + H 2 H C C H of the alkenes. They are, of course, very different compounds,
H H
H H with different physical and chemical properties. This shows the
importance of structural, rather than simply molecular, formu-
Ethylene + Hydrogen Ethane
las in referring to organic compounds.
The ethane molecule has all the hydrogen atoms possible, so The six-carbon ring structure shown in Figure 12.9A has
ethane is a saturated hydrocarbon. Unsaturated molecules are three double bonds that do not behave as do the double bonds
less stable, which means that they are more chemically reactive in the alkenes. In this six-carbon ring, the double bonds are not
than saturated molecules. localized in one place but are spread over the whole molecule.
An alkyne is a hydrocarbon with a carbon-to-carbon triple Instead of alternating single and double bonds, all the bonds
bond, and the general formula of C n H 2n–2 . The alkynes are highly are something in between. This gives the C 6 H 6 molecule in-
reactive, and the simplest one, ethyne, has a common name of creased stability. As a result, the molecule does not behave as
acetylene. Acetylene is commonly burned with oxygen gas in a other unsaturated compounds do; that is, it does not readily
welding torch because the flame reaches a temperature of about react in order to add hydrogen to the ring. The C 6 H 6 molecule
3,000°C. Acetylene is also an important raw material in the pro- is the organic compound named benzene. Organic compounds
duction of plastics. The alkynes are named as the alkenes are,
except the longest chain must contain the triple bond, and the
base name suffix is changed to -yne.
H H
C C
H C C H H C C H
H C C H H C C H
C C
A
H H
A
H H H H OH
H C H H C C H
C C H C C H
H H H H
Cyclopropane, C 3 H 6 Cyclobutane, C 4 H 8 Benzene Phenol
CH 3
H H H H
H C H H C H
CH 3
C C C C
H H H H
C C H H CH 3
H H C C
H H
H C H Toluene Xylene
(methylbenzene) (1,2-dimethylbenzene)
H H
B
Cyclopentane, C 5 H 10 Cyclohexane, C 6 H 12
B FIGURE 12.9 (A) The bonds in C 6 H 6 are something between
single and double, which gives it different chemical properties
FIGURE 12.8 (A) The “straight” chain has carbon atoms than double-bonded hydrocarbons. (B) The six-sided symbol with
that are able to rotate freely around their single bonds, sometimes a circle represents the benzene ring. Organic compounds based on
linking up in a closed ring. (B) Ring compounds of the first four the benzene ring are called aromatic hydrocarbons because of their
cycloalkanes. aromatic character.
304 CHAPTER 12 Organic Chemistry 12-6