Page 325 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 325
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 302 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch12_299-322.indd Page 302 9/3/10 6:13 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
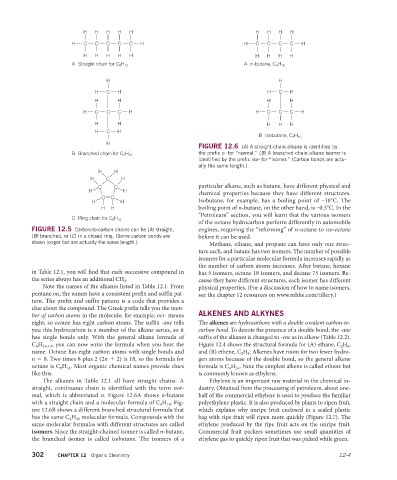
H H H H H H H H H
H C C C C C H H C C C C H
H H H H H H H H H
A Straight chain for C 5 H 12 A n-butane, C 4 H 10
H H
H C H H C H
H H H H
H C C C H H C C C H
H H H H H
H C H
B Isobutane, C 4 H 10
H
FIGURE 12.6 (A) A straight-chain alkane is identified by
the prefix n- for “normal.” (B) A branched-chain alkane isomer is
B Branched chain for C 5 H 12
identified by the prefix iso- for “isomer.” (Carbon bonds are actu-
ally the same length.)
H H
H C H
C C par ticular alkane, such as butane, have different physical and
H H
chemical properties because they have different structures.
C C
H H Isobutane, for example, has a boiling point of –10°C. The
H H boiling point of n-butane, on the other hand, is –0.5°C. In the
“Petroleum” section, you will learn that the various isomers
C Ring chain for C 5 H 10
of the octane hydrocarbon perform differently in automobile
FIGURE 12.5 Carbon-to-carbon chains can be (A) straight, engines, requiring the “reforming” of n-octane to iso-octane
(B) branched, or (C) in a closed ring. (Some carbon bonds are before it can be used.
drawn longer but are actually the same length.) Methane, ethane, and propane can have only one struc-
ture each, and butane has two isomers. The number of possible
isomers for a particular molecular formula increases rapidly as
the number of carbon atoms increases. After butane, hexane
in Table 12.1, you will find that each successive compound in has 5 isomers, octane 18 isomers, and decane 75 isomers. Be-
the series always has an additional CH 2 . cause they have different structures, each isomer has different
Note the names of the alkanes listed in Table 12.1. From physical properties. (For a discussion of how to name isomers,
pentane on, the names have a consistent prefix and suffix pat- see the chapter 12 resources on www.mhhe.com/tillery.)
tern. The prefix and suffix pattern is a code that provides a
clue about the compound. The Greek prefix tells you the num-
ber of carbon atoms in the molecule; for example, oct- means ALKENES AND ALKYNES
eight, so octane has eight carbon atoms. The suffix -ane tells The alkenes are hydrocarbons with a double covalent carbon-to-
you this hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series, so it carbon bond. To denote the presence of a double bond, the -ane
has single bonds only. With the general alkane formula of suffix of the alkanes is changed to -ene as in alkene (Table 12.2).
C n H 2n+2 , you can now write the formula when you hear the Figure 12.4 shows the structural formula for (A) ethane, C 2 H 6 ,
name. Octane has eight carbon atoms with single bonds and and (B) ethene, C 2 H 4 . Alkenes have room for two fewer hydro-
n = 8. Two times 8 plus 2 (2n + 2) is 18, so the formula for gen atoms because of the double bond, so the general alkene
octane is C 8 H 18 . Most organic chemical names provide clues formula is C n H 2n . Note the simplest alkene is called ethene but
like this. is commonly known as ethylene.
The alkanes in Table 12.1 all have straight chains. A Ethylene is an important raw material in the chemical in-
straight, continuous chain is identified with the term nor- dustry. Obtained from the processing of petroleum, about one-
mal, which is abbreviated n. Figure 12.6A shows n-butane half of the commercial ethylene is used to produce the familiar
with a straight chain and a molecular formula of C 4 H 10 . Fig- polyethylene plastic. It is also produced by plants to ripen fruit,
ure 12.6B shows a different branched structural formula that which explains why unripe fruit enclosed in a sealed plastic
has the same C 4 H 10 molecular formula. Compounds with the bag with ripe fruit will ripen more quickly (Figure 12.7). The
same molecular formulas with different structures are called ethylene produced by the ripe fruit acts on the unripe fruit.
isomers. Since the straight-chained isomer is called n-butane, Commercial fruit packers sometimes use small quantities of
the branched isomer is called isobutane. The isomers of a ethylene gas to quickly ripen fruit that was picked while green.
302 CHAPTER 12 Organic Chemistry 12-4