Page 419 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 419
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch15_377-404.indd Page 396 9/3/10 6:17 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch15_377-404.indd Page 396 9/3/10 6:17 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
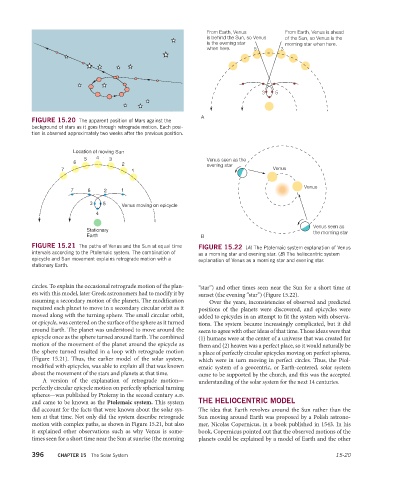
From Earth, Venus From Earth, Venus is ahead
is behind the Sun, so Venus of the Sun, so Venus is the
is the evening star morning star when here.
when here. 5 3
3 5
A
FIGURE 15.20 The apparent position of Mars against the
background of stars as it goes through retrograde motion. Each posi-
tion is observed approximately two weeks after the previous position.
Venus seen as the
evening star
Venus
Venus
Venus seen as
the morning star
B
FIGURE 15.21 The paths of Venus and the Sun at equal time FIGURE 15.22 (A) The Ptolemaic system explanation of Venus
intervals according to the Ptolemaic system. The combination of as a morning star and evening star. (B) The heliocentric system
epicycle and Sun movement explains retrograde motion with a explanation of Venus as a morning star and evening star.
stationary Earth.
circles. To explain the occasional retrograde motion of the plan- “star”) and other times seen near the Sun for a short time at
ets with this model, later Greek astronomers had to modify it by sunset (the evening “star”) (Figure 15.22).
assuming a secondary motion of the planets. The modification Over the years, inconsistencies of observed and predicted
required each planet to move in a secondary circular orbit as it positions of the planets were discovered, and epicycles were
moved along with the turning sphere. The small circular orbit, added to epicycles in an attempt to fit the system with observa-
or epicycle, was centered on the surface of the sphere as it turned tions. The system became increasingly complicated, but it did
around Earth. The planet was understood to move around the seem to agree with other ideas of that time. Those ideas were that
epicycle once as the sphere turned around Earth. The combined (1) humans were at the center of a universe that was created for
motion of the movement of the planet around the epicycle as them and (2) heaven was a perfect place, so it would naturally be
the sphere turned resulted in a loop with retrograde motion a place of perfectly circular epicycles moving on perfect spheres,
( Figure 15.21). Thus, the earlier model of the solar system, which were in turn moving in perfect circles. Thus, the Ptol-
modified with epicycles, was able to explain all that was known emaic system of a geocentric, or Earth-centered, solar system
about the movement of the stars and planets at that time. came to be supported by the church, and this was the accepted
A version of the explanation of retrograde motion— understanding of the solar system for the next 14 centuries.
perfectly circular epicycle motion on perfectly spherical turning
spheres—was published by Ptolemy in the second century a.d.
and came to be known as the Ptolemaic system. This system THE HELIOCENTRIC MODEL
did account for the facts that were known about the solar sys- The idea that Earth revolves around the Sun rather than the
tem at that time. Not only did the system describe retrograde Sun moving around Earth was proposed by a Polish astrono-
motion with complex paths, as shown in Figure 15.21, but also mer, Nicolas Copernicus, in a book published in 1543. In his
it explained other observations such as why Venus is some- book, Copernicus pointed out that the observed motions of the
times seen for a short time near the Sun at sunrise (the morning planets could be explained by a model of Earth and the other
396 CHAPTER 15 The Solar System 15-20