Page 14 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 14
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
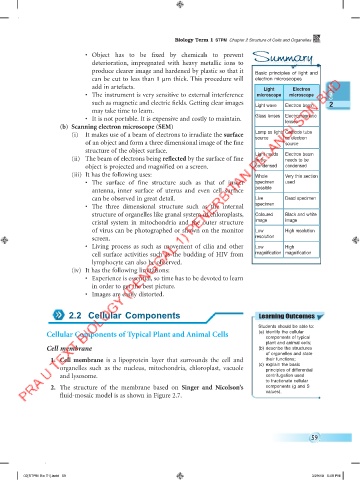
• Object has to be fixed by chemicals to prevent Summary
deterioration, impregnated with heavy metallic ions to
produce clearer image and hardened by plastic so that it Basic principles of light and
can be cut to less than 1 µm thick. This procedure will electron microscopes
add in artefacts. Light Electron
• The instrument is very sensitive to external interference microscope microscope
such as magnetic and electric fields. Getting clear images Light wave Electron beam 2
may take time to learn.
• It is not portable. It is expensive and costly to maintain. Glass lenses Electromagnetic
lenses
(b) Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
(i) It makes use of a beam of electrons to irradiate the surface Lamp as light Cathode tube
as electron
source
of an object and form a three dimensional image of the fine source
structure of the object surface. Light needs Electron beam
(ii) The beam of electrons being reflected by the surface of fine to be needs to be
object is projected and magnified on a screen. condensed condensed
(iii) It has the following uses: Whole Very thin section
• The surface of fine structure such as that of insect specimen used
possible
antenna, inner surface of uterus and even cell surface
can be observed in great detail. Live Dead specimen
• The three dimensional structure such as the internal specimen
structure of organelles like granal system of chloroplasts, Coloured Black and white
cristal system in mitochondria and the outer structure image image
of virus can be photographed or shown on the monitor Low High resolution
screen. resolution
• Living process as such as movement of cilia and other Low High
cell surface activities such as the budding of HIV from magnification magnification
lymphocyte can also be observed.
(iv) It has the following limitations:
• Experience is essential, so time has to be devoted to learn
in order to get the best picture.
• Images are easily distorted.
2.2 Cellular Components Learning Outcomes
Students should be able to:
Cellular Components of Typical Plant and Animal Cells (a) identify the cellular
components of typical
plant and animal cells;
Cell membrane (b) describe the structures
of organelles and state
1. Cell membrane is a lipoprotein layer that surrounds the cell and their functions;
organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, vacuole (c) explain the basic
principles of differential
and lysosome. centrifugation used
to fractionate cellular
2. The structure of the membrane based on Singer and Nicolson’s components (g and S
values).
fluid-mosaic model is as shown in Figure 2.7.
59
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 59 3/29/18 5:08 PM