Page 50 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 50
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
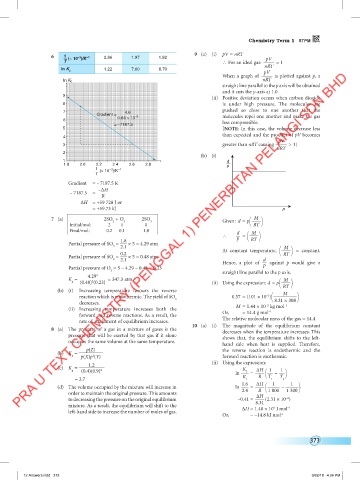
6 1 (× 10 )/K –1 2.86 1.97 1.82 9 (a) (i) pV = nRT pV
–3
T ∴ For an ideal gas: —––— = 1
ln K 1.22 7.60 8.70 nRT
c pV
When a graph of —––— is plotted against p, a
In K c nRT
straight line parallel to the p axis will be obtained
and it cuts the y-axis at 1.0
9
(ii) Positive deviation occurs when carbon dioxide
8 is under high pressure. The molecules are
pushed so close to one another that the
7 4.6
Gradient = molecules repel one another and make the gas
0.64 × 10 –3
6 less compressible.
= –7187.5
5 [NOTE: In this case, the volume decrease less
than expected and the product of pV becomes
4
pV
3 greater than nRT causing —––— > 1]
nRT
2
(b) (i)
1 d
1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 p
1 (× 10 )/K –1
–3
T
Gradient = – 7187.5 K
–∆H
– 7187.5 =
R
∆H = +59 728 J or
= +59.73 kJ p
M
7 (a) 2SO + O 2 2SO 3 Given: d = p —–––
2
Initial/mol: 2 1 0 RT
Final/mol: 0.2 0.1 1.8 d M
p
∴ — = —–––
1.8 RT
Partial pressure of SO = × 5 = 4.29 atm
3 2.1 M
0.2 At constant temperature, —––– = constant.
RT
Partial pressure of SO = × 5 = 0.48 atm
2 2.1 d
Hence, a plot of — against p would give a
p
Partial pressure of O = 5 – 4.29 – 0.48 = 0.23
2
4.29 2 straight line parallel to the p axis.
K = = 347.3 atm –1 M
p (0.48) (0.23) (ii) Using the expression: d = p —–––
2
(b) (i) Increasing temperature favours the reverse RT
M
reaction which is endothermic. The yield of SO 0.57 = (101 × 10 ) ————–––––
–3
3
decreases. –2 8.31 × 308
–1
(ii) Increasing temperature increases both the Or, M = 1.44 × 10 kg mol
–1
= 14.4 g mol
forward and reverse reactions. As a result, the The relative molecular mass of the gas = 14.4
rate of attainment of equilibrium increases.
10 (a) (i) The magnitude of the equilibrium constant
8 (a) The pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases is the decreases when the temperature increases. This
pressure that will be exerted by that gas if it alone shows that, the equilibrium shifts to the left-
occupies the same volume at the same temperature.
hand side when heat is supplied. Therefore,
p(Z)
(b) K = the reverse reaction is endothermic and the
2
p p(X)p (Y) forward reaction is exothermic.
1.2 (ii) Using the expression:
(c) K = K
∆H
1
1
p (0.4)(0.9) 2 ln —–– = —––– —– – —–
2
= 3.7 K 1 R T 1 T 2
1
1.6
1
∆H
(d) The volume occupied by the mixture will increase in ln —–– = —––– ——––– – ——–––
R
order to maintain the original pressure. This amounts 2.4 ∆H 1 000 1 300
to decreasing the pressure on the original equilibrium –0.41 = —–––(2.31 × 10 )
–4
8.31
mixture. As a result, the equilibrium will shift to the 4 –1
left-hand side to increase the number of moles of gas. ∆H = 1.48 × 10 J mol
Or, = –14.8 kJ mol
–1
373
12 Answers.indd 373 3/26/18 4:06 PM