Page 45 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 45
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
(c) Presence of dissolved salts makes the orderly (b) Increasing the pressure on the carbon dioxide gas
arrangement of the ice crystal structure more pushes the molecules close together. The attractive
difficult to form. force ‘binds’ the molecules in clusters causing the gas
The volume of water in the sea is much larger. to liquefied.
12 (a) The temperature and pressure where the three (c) When the liquefied carbon dioxide is released, it
phases of a substance can exist in equilibrium. absorbs heat from the surroundings and vaporised.
(b) Refer to text This causes the water vapour in the surrounding air
(c) Decreases. Presence of another substance makes the to condense causing a white mist to form.
solid crystal structure of CO more difficult to form.
2
(d) Because it’s triple point pressure is higher than 1 atm. Chapter 5 Reaction Kinetics
13 (a) (i) Melting point
(ii) Boiling point Quick Check 5.1
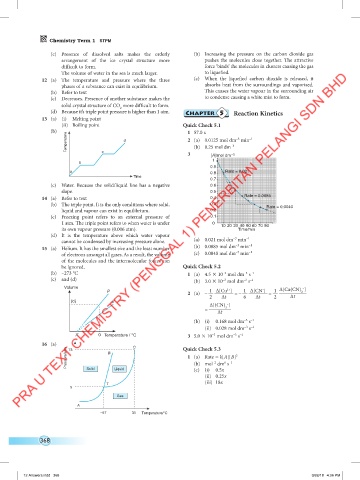
(b) 1 57.0 s
Temperature d 2 (a) 0.0125 mol dm min
–3
–1
–3
(b) 0.25 mol dm
3 [A]/mol dm –3
c
1
b
0.9
a Rate = 0.021
0.8
Time
0.7
(c) Water. Because the solid/liquid line has a negative 0.6
slope. 0.5
14 (a) Refer to text 0.4 Rate = 0.0085
(b) The triple point. It is the only conditions where solid, 0.3 Rate = 0.0040
liquid and vapour can exist in equilibrium. 0.2
(c) Freezing point refers to an external pressure of 0.1
1 atm. The triple point refers to when water is under 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
its own vapour pressure (0.006 atm). Time/min
(d) It is the temperature above which water vapour –3 –1
cannot be condensed by increasing pressure alone. (a) 0.021 mol dm min
–3
15 (a) Helium. It has the smallest size and the least number (b) 0.0085 mol dm min –1
–1
–3
of electrons amongst all gases. As a result, the volume (c) 0.0040 mol dm min
of the molecules and the intermolecular forces can
be ignored. Quick Check 5.2
(b) –273 °C 1 (a) 4.5 10 mol dm s
–3
–3 –1
(c) and (d) (b) 3.0 10 mol dm s
–3 –1
–3
Volume –
2+
p 1 ∆[Cu ] 1 ∆[CN ] 1 ∆[Cu(CN) ]
–
2
2 (a) – 2 ∆t = – 6 ∆t = ∆t
2
(d) p’ ∆[(CN) ]
–
= ∆t 2
–3 –1
(b) (i) 0.168 mol dm s
(ii) 0.028 mol dm s
–3 –1
–3
–3 –1
X 0 Temperature / °C 3 5.0 10 mol dm s
16 (a) 73 C Quick Check 5.3
Pressure/atm B 1 (a) Rate = k[A][B]
2
–2
6 –1
(b) mol dm s
(c) (i) 0.5x
Solid
Liquid
(ii) 0.25x
(iii) 18x
T
5
Gas
A
–57 31 Temperature/°C
368
12 Answers.indd 368 3/26/18 4:06 PM