Page 52 - ACE YR IGCSE A TOP APPROACH TO CHEM
P. 52
(b) Any one from: (ii) Sulfur reacts with oxygen to form sulfur
Use: Galvanising iron / steel [1] dioxide and escapes. [1]
Property: Resistant to corrosion [1] S + O ➞ SO [1]
2 2
Or (iii) Silicon dioxide is acidic. [1]
Use: For torch batteries [1] It can be neutralised by calcium oxide.
Property: Conductor of electricity [1] Silicon dioxide + calcium oxide ➞ calcium
(c) Any one from: silicate [1]
Use: Electrical wiring [1] (iv) Phosphorus oxide is acidic. [1]
Property: Good conductor of electricity / It can be neutralised by calcium oxide.
Ductile [1] Phosphorus oxide + calcium oxide ➞
Or calcium phosphate [1]
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
Use: Saucepans / saucepan bases [1] (b) (i) Any one from: [1]
Property: Conductor of heat / Malleable / • For buildings
Tough [1]
• Car bodies
(d) Any one from: • Ships
Use: Cutlery / Food containers [1] • Machinery
Property: Resistant to corrosion / Hard / (ii) Particles are arranged in layers. [1]
Waterproof [1] Can slide over each other easily. [1]
Or (iii) More carbon atoms in high-carbon steel.
Use: Medical tools [1] [1]
Property: Resistant to corrosion / Hard / The layers cannot slide over each other. [1]
Waterproof [1]
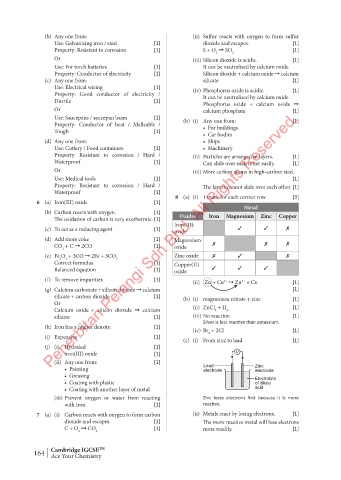
8 (a) (i) 1 mark for each correct row [3]
6 (a) Iron(III) oxide [1]
Metal
(b) Carbon reacts with oxygen. [1]
The oxidation of carbon is very exothermic. [1] Oxides Iron Magnesium Zinc Copper
Iron(III)
(c) To act as a reducing agent [1] oxide 3 3 7
(d) Add more coke [1] Magnesium
CO + C ➞ 2CO [1] oxide 7 7 7
2
(e) Fe O + 3CO ➞ 2Fe + 3CO 2 Zinc oxide 7 3 7
2
3
Correct formulas [1] Copper(II)
Balanced equation [1] oxide 3 3 3
(f) To remove impurities [1] (ii) Zn + Cu ➞ Zn + Cu [1]
2+
2+
(g) Calcium carbonate + silicon dioxide ➞ calcium [1]
silicate + carbon dioxide [1] (b) (i) magnesium nitrate + zinc [1]
Or
Calcium oxide + silicon dioxide ➞ calcium (ii) ZnCl + H [1]
2
2
silicate [1] (iii) No reaction [1]
Silver is less reactive than potassium.
(h) Iron has a higher density. [1]
(iv) Br + 2Cl [1]
–
(i) Expensive [1] 2
(c) (i) From zinc to lead [1]
(j) (i) Hydrated [1]
iron(III) oxide [1] V
(ii) Any one from: [1]
• Painting Lead Zinc
electrode
electrode
• Greasing Electrolyte
• Coating with plastic of dilute
• Coating with another layer of metal acid
(iii) Prevent oxygen or water from reacting Zinc loses electrons first because it is more
with iron [1] reactive.
7 (a) (i) Carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon (ii) Metals react by losing electrons. [1]
dioxide and escapes. [1] The more reactive metal will lose electrons
C + O ➞ CO [1] more readily. [1]
2
2
Cambridge IGCSE TM
164 Ace Your Chemistry
Answers.indd 164 3/4/22 3:54 PM