Page 47 - ACE YR IGCSE A TOP APPROACH TO CHEM
P. 47
3 B 7 C
Carbon forms a giant covalent structure which has a high
melting point.
Chromium is a transition element. It has a high melting
The atomic radius increases as going down Group I point.
because the number of shells / orbits increases. Caesium is a metal. As going down the group, the melting
As the atomic radius increases down the group, the point decreases. Caesium has a low melting point.
melting point decreases.
The attraction between the nucleus and electrons in the 8 D
outer shell is weaker as the distance increases. The weak The roman number represents the oxidation state of an
attraction also causes them to become more reactive element. It is important because some elements have
when down the group. variable oxidation states. Iron shows two oxidation states,
2Na + 2H O ➞ 2NaOH + H 2 that is +2 and +3. So, (II) and (III) are used in the naming.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
2
NaOH is alkaline. 9 B
4 C W is sodium. Sodium is very reactive. Sodium reacts with
The element located above iodine in the Periodic Table cold water.
is bromine. Bromine is a red-brown liquid at room X is neon. Neon is unreactive.
temperature. Bromine is more reactive than iodine. Y is manganese. Manganese is a transition metal. It has
variable oxidation states.
5 B Z is silicon. Silicon forms macromolecules with oxygen.
The proton number of helium is 2. It is unreactive.
The proton number of beryllium is 4. Beryllium is a 10 A
metal. It can react with oxygen to form beryllium oxide. Hydrogen is flammable. It can trigger an explosion
The proton number of carbon is 6. Carbon reacts with when it gets in touch with fire or sparks. Helium is an
oxygen to form carbon dioxide. unreactive gas. So, it is safe.
The proton number of oxygen is 8. Oxygen can form
diatomic molecules with each other but cannot form Part 2: Structured Questions
oxides. 1 (a) Increasing proton number [1]
The proton number of neon is 10. It is unreactive.
(b) React in the similar way [1]
6 B
Rubidium is Group I element. It reacts with bromine to Have the same number of electrons in the
form an ionic compound. Rb loses 1 electron to form outer shell / Have the same number of valence
–
+
Rb . Br gains 1 electron to form Br . So, the chemical electrons [1]
formula for rubidium bromide is RbBr. Since rubidium is
Group I element, it cannot form a coloured compound. (c) The number of shells [1]
(d)
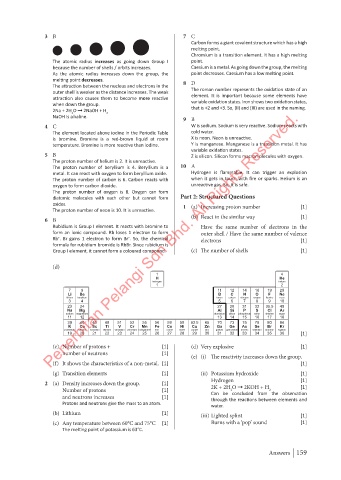
1 4
H He
hydrogen helium
1 2
7 9 11 12 14 16 19 20
Li Be B C N O F Ne
lithium beryllium boron carbon nitrogen oxygen fluorine neon
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
23 24 27 28 31 32 35.5 40
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
sodium magnesium aluminium silicon phosphorus sulfur chlorine argon
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
39 40 45 48 51 52 55 56 59 59 63.5 65 70 73 75 79 80 84
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
potassium calcium scandium titanium vanadium chromium manganese iron cobalt nickel copper zinc gallium germanium arsenic selenium bromine krypton
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 [1]
(e) Number of protons + [1] (d) Very explosive [1]
number of neutrons [1]
(e) (i) The reactivity increases down the group.
(f) It shows the characteristics of a non-metal. [1] [1]
(g) Transition elements [1] (ii) Potassium hydroxide [1]
Hydrogen [1]
2 (a) Density increases down the group. [1] 2K + 2H O ➞ 2KOH + H [1]
Number of protons [1] Can be concluded from the observation
2
2
and neutrons increases [1] through the reactions between elements and
Protons and neutrons give the mass to an atom. water.
(b) Lithium [1] (iii) Lighted splint [1]
(c) Any temperature between 60°C and 75°C [1] Burns with a ‘pop’ sound [1]
The melting point of potassium is 63°C.
Answers 159
Answers.indd 159 3/4/22 3:54 PM