Page 17 - Ranger SPM 2022 Biology
P. 17
Biology SPM Chapter 2 Leaf Structure and Function
2.1 Structure of a Leaf
1. Leaf is the main organ of plant for gaseous exchange, transpiration, and
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
photosynthesis.
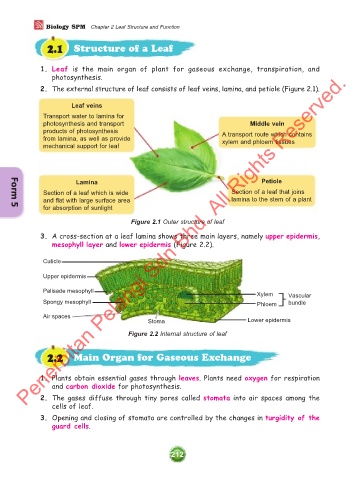
2. The external structure of leaf consists of leaf veins, lamina, and petiole (Figure 2.1).
Leaf veins
Transport water to lamina for
photosynthesis and transport Middle vein
products of photosynthesis A transport route which contains
from lamina, as well as provide xylem and phloem tissues
mechanical support for leaf
Lamina Petiole
Section of a leaf which is wide Section of a leaf that joins
and flat with large surface area lamina to the stem of a plant
for absorption of sunlight
Form 5
Figure 2.1 Outer structure of leaf
3. A cross-section at a leaf lamina shows three main layers, namely upper epidermis,
mesophyll layer and lower epidermis (Figure 2.2).
Cuticle
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll Xylem Vascular
Spongy mesophyll Phloem bundle
Air spaces
Stoma Lower epidermis
Figure 2.2 Internal structure of leaf
2.2 Main Organ for Gaseous Exchange
1. Plants obtain essential gases through leaves. Plants need oxygen for respiration
and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
2. The gases diffuse through tiny pores called stomata into air spaces among the
cells of leaf.
3. Opening and closing of stomata are controlled by the changes in turgidity of the
guard cells.
212
F5 Chapter 2.indd 212 3/29/22 4:35 PM