Page 18 - Ranger SPM 2022 Biology
P. 18
Biology SPM Chapter 2 Leaf Structure and Function
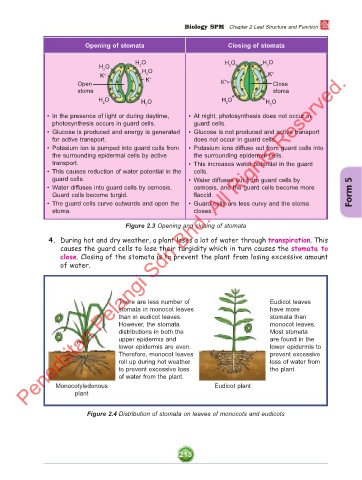
Opening of stomata Closing of stomata
H O H O H O
H O 2 2 2
2 H O
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
K + 2 + K +
Open K K + Close
stoma stoma
H O H O
2 H O 2 H O
2 2
• In the presence of light or during daytime, • At night, photosynthesis does not occur in
photosynthesis occurs in guard cells. guard cells.
• Glucose is produced and energy is generated • Glucose is not produced and active transport
for active transport. does not occur in guard cells.
• Potasium ion is pumped into guard cells from • Potasium ions diffuse out from guard cells into
the surrounding epidermal cells by active the surrounding epidermal cells.
transport. • This increases water potential in the guard
• This causes reduction of water potential in the cells.
guard cells. • Water diffuses out from guard cells by
• Water diffuses into guard cells by osmosis. osmosis, and the guard cells become more
Guard cells become turgid. flaccid. Form 5
• The guard cells curve outwards and open the • Guard cells are less curvy and the stoma
stoma. closes.
Figure 2.3 Opening and closing of stomata
4. During hot and dry weather, a plant loses a lot of water through transpiration. This
causes the guard cells to lose their turgidity which in turn causes the stomata to
close. Closing of the stomata is to prevent the plant from losing excessive amount
of water.
There are less number of Eudicot leaves
stomata in monocot leaves have more
than in eudicot leaves. stomata than
However, the stomata monocot leaves.
distributions in both the Most stomata
upper epidermis and are found in the
lower epidermis are even. lower epidermis to
Therefore, monocot leaves prevent excessive
roll up during hot weather loss of water from
to prevent excessive loss the plant.
of water from the plant.
Monocotyledonous Eudicot plant
plant
Figure 2.4 Distribution of stomata on leaves of monocots and eudicots
213
F5 Chapter 2.indd 213 3/29/22 4:35 PM