Page 243 - The Design Thinking Playbook
P. 243
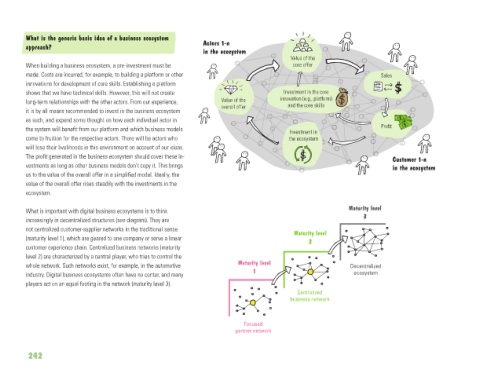
What is the generic basic idea of a business ecosystem
approach? Actors 1-n
in the ecosystem
Value of the
When building a business ecosystem, a pre-investment must be core offer
made. Costs are incurred, for example, to building a platform or other Sales
innovations for development of core skills. Establishing a platform
shows that we have technical skills. However, this will not create Investment in the core
long-term relationships with the other actors. From our experience, Value of the innovation (e.g., platform)
and the core skills
it is by all means recommended to invest in the business ecosystem overall offer
as such, and expend some thought on how each individual actor in
the system will benefit from our platform and which business models Investment in Profit
come to fruition for the respective actors. There will be actors who the ecosystem
will lose their livelihoods in this environment on account of our ideas.
The profit generated in the business ecosystem should cover these in- Customer 1-n
vestments as long as other business models don’t copy it. This brings in the ecosystem
us to the value of the overall offer in a simplified model. Ideally, the
value of the overall offer rises steadily with the investments in the
ecosystem.
What is important with digital business ecosystems is to think Maturity level
increasingly in decentralized structures (see diagram). They are 3
not centralized customer-supplier networks in the traditional sense Maturity level
(maturity level 1), which are geared to one company or serve a linear 2
customer experience chain. Centralized business networks (maturity
level 2) are characterized by a central player, who tries to control the
whole network. Such networks exist, for example, in the automotive Maturity level Decentralized
industry. Digital business ecosystems often have no center, and many 1 ecosystem
players act on an equal footing in the network (maturity level 3).
Centralized
business network
Focused
partner network
242