Page 32 - Unit2.docx
P. 32
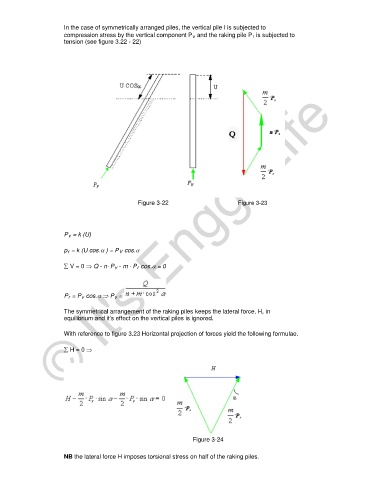
In the case of symmetrically arranged piles, the vertical pile I is subjected to
compression stress by the vertical component P v and the raking pile P r is subjected to
tension (see figure 3.22 - 22)
© It's Engg. Life
Figure 3-22 Figure 3-23
P v = k (U)
p r = k (U cos.α ) = P V cos.α
∑ V = 0 ⇒ Q - n⋅ P v - m ⋅ P r cos.α = 0
P r = P v cos.α ⇒ P v =
The symmetrical arrangement of the raking piles keeps the lateral force, H, in
equilibrium and it’s effect on the vertical piles is ignored.
With reference to figure 3.23 Horizontal projection of forces yield the following formulae.
∑ H = 0 ⇒
Figure 3-24
NB the lateral force H imposes torsional stress on half of the raking piles.