Page 260 - Office Practice and Accounting 10
P. 260
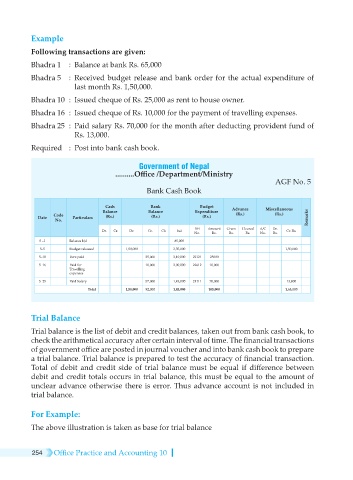
Example
Following transactions are given:
Bhadra 1 : Balance at bank Rs. 65,000
Bhadra 5 : Received budget release and bank order for the actual expenditure of
last month Rs. 1,50,000.
Bhadra 10 : Issued cheque of Rs. 25,000 as rent to house owner.
Bhadra 16 : Issued cheque of Rs. 10,000 for the payment of travelling expenses.
Bhadra 25 : Paid salary Rs. 70,000 for the month after deducting provident fund of
Rs. 13,000.
Required : Post into bank cash book.
Government of Nepal
..........Office /Department/Ministry
AGF No. 5
Bank Cash Book
Cash Bank Budget
Balance Balance Expenditure Advance Miscellaneous
Code (Rs.) (Rs.)
Date Particulars (Rs.) (Rs.) (Rs.) Remarks
No.
BH Amount Given Cleared A/C Dr.
Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Ch bal Cr. Rs.
No. Rs. Rs. Rs. No. Rs.
5 –1 Balance b/d 85,000
5–5 Budget released 1,50,000 2,35,000 1,50,000
5–10 Rent paid 25,000 2,10,000 22121 25000
5–16 Paid for 10,000 2,00,000 22612 10,000
Travelling
expenses
5–25 Paid Salary 57,000 1,43,000 21111 70,000 13,000
Total 1,50,000 92,000 1,43,000 105,000 1,63,000
Trial Balance
Trial balance is the list of debit and credit balances, taken out from bank cash book, to
check the arithmetical accuracy after certain interval of time. The financial transactions
of government office are posted in journal voucher and into bank cash book to prepare
a trial balance. Trial balance is prepared to test the accuracy of financial transaction.
Total of debit and credit side of trial balance must be equal if difference between
debit and credit totals occurs in trial balance, this must be equal to the amount of
unclear advance otherwise there is error. Thus advance account is not included in
trial balance.
For Example:
The above illustration is taken as base for trial balance
254 Office Practice and Accounting 10