Page 63 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 63
44 UNIT I Evolution of Nursing Theories
process” (p. 16) and is recognized as the first nursing resource person, teacher, leader, surrogate, and coun-
theory textbook since Nightingale’s work in the 1850s. selor (Figure 5-3).
She discussed four psychobiological experiences that Peplau had professional relationships with others
compel destructive or constructive patient responses, in psychiatry, medicine, education, and sociology
as follows: needs, frustrations, conflicts, and anxieties. that influenced her view of what a profession is and
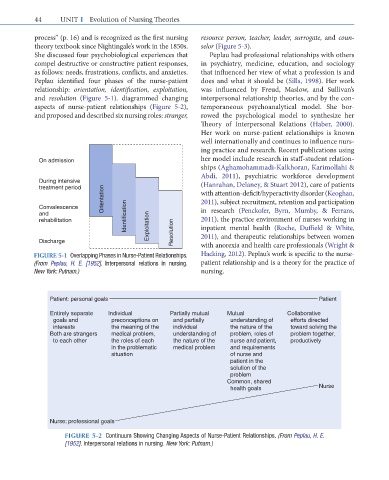
Peplau identified four phases of the nurse-patient does and what it should be (Sills, 1998). Her work
relationship: orientation, identification, exploitation, was influenced by Freud, Maslow, and Sullivan’s
and resolution (Figure 5-1). diagrammed changing interpersonal relationship theories, and by the con-
aspects of nurse-patient relationships (Figure 5-2), temporaneous psychoanalytical model. She bor-
and proposed and described six nursing roles: stranger, rowed the psychological model to synthesize her
Theory of Interpersonal Relations (Haber, 2000).
Her work on nurse-patient relationships is known
well internationally and continues to influence nurs-
ing practice and research. Recent publications using
On admission her model include research in staff-student relation-
ships (Aghamohammadi-Kalkhoran, Karimollahi &
Abdi, 2011), psychiatric workforce development
During intensive (Hanrahan, Delaney, & Stuart 2012), care of patients
treatment period with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (Keoghan,
Convalescence Orientation 2011), subject recruitment, retention and participation
in research (Penckofer, Byrn, Mumby, & Ferrans,
and Identification
rehabilitation Exploitation 2011), the practice environment of nurses working in
inpatient mental health (Roche, Duffield & White,
Discharge Resolution 2011), and therapeutic relationships between women
with anorexia and health care professionals (Wright &
FIGURE 5-1 OverlappingPhasesinNurse-PatientRelationships. Hacking, 2012). Peplau’s work is specific to the nurse-
(From Peplau, H. E. [1952]. Interpersonal relations in nursing. patient relationship and is a theory for the practice of
New York: Putnam.) nursing.
Patient: personal goals Patient
Entirely separate Individual Partially mutual Mutual Collaborative
goals and preconceptions on and partially understanding of efforts directed
interests the meaning of the individual the nature of the toward solving the
Both are strangers medical problem, understanding of problem, roles of problem together,
to each other the roles of each the nature of the nurse and patient, productively
in the problematic medical problem and requirements
situation of nurse and
patient in the
solution of the
problem
Common, shared
health goals Nurse
Nurse: professional goals
FIGURE 5-2 ContinuumShowingChangingAspectsofNurse-PatientRelationships.(From Peplau, H. E.
[1952]. Interpersonalrelationsinnursing. New York: Putnam.)