Page 116 - Class-11-Physics-Part-1_Neat
P. 116
102 PHYSICS
approximately true. Yet they are very useful in Answer The forces acting on a block of mass m
practical calculations in mechanics. at rest on an inclined plane are (i) the weight
Thus, when two bodies are in contact, each mg acting vertically downwards (ii) the normal
experiences a contact force by the other. Friction, force N of the plane on the block, and (iii) the
by definition, is the component of the contact force static frictional force f opposing the impending
s
parallel to the surfaces in contact, which opposes motion. In equilibrium, the resultant of these
impending or actual relative motion between the forces must be zero. Resolving the weight mg
two surfaces. Note that it is not motion, but along the two directions shown, we have
relative motion that the frictional force opposes. m g sin θ = f , m g cos θ = N
s
Consider a box lying in the compartment of a train As θ increases, the self-adjusting frictional force
that is accelerating. If the box is stationary
relative to the train, it is in fact accelerating along f s increases until at θ = θ max , f s achieves its
with the train. What forces cause the acceleration maximum value, ( ) = µ N.
f
s
of the box? Clearly, the only conceivable force in max s
the horizontal direction is the force of friction. If Therefore,
there were no friction, the floor of the train would tan θ = µ or θ = tan µ
–1
slip by and the box would remain at its initial max s max s
position due to inertia (and hit the back side of When θ becomes just a little more than θ ,
max
the train). This impending relative motion is there is a small net force on the block and it
opposed by the static friction f . Static friction begins to slide. Note that θ depends only on
s max
provides the same acceleration to the box as that µ and is independent of the mass of the block.
s
of the train, keeping it stationary relative to the
train. For θ max = 15°,
µ = tan 15°
Example 5.7 Determine the maximum s = 0.27 t
t
acceleration of the train in which a box
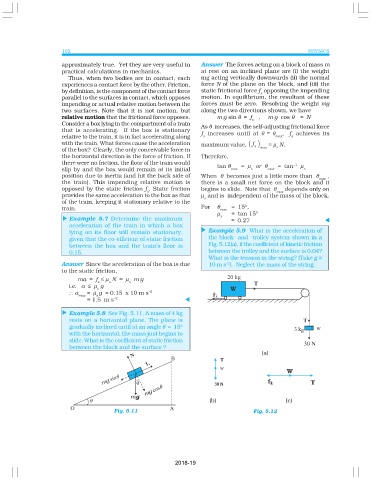
lying on its floor will remain stationary, t Example 5.9 What is the acceleration of
given that the co-efficient of static friction the block and trolley system shown in a
between the box and the train’s floor is Fig. 5.12(a), if the coefficient of kinetic friction
0.15. between the trolley and the surface is 0.04?
What is the tension in the string? (Take g =
Answer Since the acceleration of the box is due 10 m s ). Neglect the mass of the string.
-2
to the static friction,
ma = f ≤ µ N = µ m g
s s s
i.e. a ≤ µ g
s
∴ a = µ g = 0.15 x 10 m s –2
max s
= 1.5 m s –2 t
Example 5.8 See Fig. 5.11. A mass of 4 kg
t
rests on a horizontal plane. The plane is
gradually inclined until at an angle θ = 15°
with the horizontal, the mass just begins to
slide. What is the coefficient of static friction
between the block and the surface ?
(a)
(b) (c)
Fig. 5.11 Fig. 5.12
2018-19