Page 219 - Engineering Mathematics Workbook_Final
P. 219
Numerical Methods
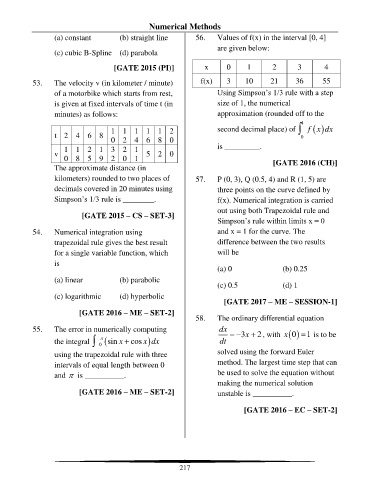
(a) constant (b) straight line 56. Values of f(x) in the interval [0, 4]
are given below:
(c) cubic B-Spline (d) parabola
[GATE 2015 (PI)] x 0 1 2 3 4
53. The velocity v (in kilometer / minute) f(x) 3 10 21 36 55
of a motorbike which starts from rest, Using Simpson’s 1/3 rule with a step
is given at fixed intervals of time t (in size of 1, the numerical
minutes) as follows: approximation (rounded off to the
1 1 1 1 1 2 second decimal place) of 4 f ( ) x dx
t 2 4 6 8 0
0 2 4 6 8 0
1 1 2 1 3 2 1 is _________.
v 5 2 0
0 8 5 9 2 0 1 [GATE 2016 (CH)]
The approximate distance (in
kilometers) rounded to two places of 57. P (0, 3), Q (0.5, 4) and R (1, 5) are
decimals covered in 20 minutes using three points on the curve defined by
Simpson’s 1/3 rule is ________. f(x). Numerical integration is carried
out using both Trapezoidal rule and
[GATE 2015 – CS – SET-3]
Simpson’s rule within limits x = 0
54. Numerical integration using and x = 1 for the curve. The
trapezoidal rule gives the best result difference between the two results
for a single variable function, which will be
is
(a) 0 (b) 0.25
(a) linear (b) parabolic
(c) 0.5 (d) 1
(c) logarithmic (d) hyperbolic
[GATE 2017 – ME – SESSION-1]
[GATE 2016 – ME – SET-2]
58. The ordinary differential equation
55. The error in numerically computing dx = − 3x + , with ( ) 0 = is to be
2
1
x
the integral 0 (sin x + cos ) x dx dt
using the trapezoidal rule with three solved using the forward Euler
intervals of equal length between 0 method. The largest time step that can
and is __________. be used to solve the equation without
making the numerical solution
[GATE 2016 – ME – SET-2] unstable is __________.
[GATE 2016 – EC – SET-2]
217