Page 188 - Advanced Course
P. 188
KNX ADVANCED COURSE
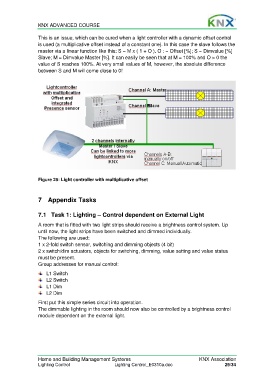
This is an issue, which can be cured when a light controller with a dynamic offset control
is used (a multiplicative offset instead of a constant one). In this case the slave follows the
master via a linear function like this: S = M x ( 1 + O ). O : = Offset [%]; S = Dimvalue [%]
Slave; M = Dimvalue Master [%]. It can easily be seen that at M = 100% and O > 0 the
value of S reaches 100%. At very small values of M, however, the absolute difference
between S and M will come close to 0!
Figure 25: Light controller with multiplicative offset
7 Appendix Tasks
7.1 Task 1: Lighting – Control dependent on External Light
A room that is fitted with two light strips should receive a brightness control system. Up
until now, the light strips have been switched and dimmed individually.
The following are used:
1 x 2-fold switch sensor, switching and dimming objects (4 bit)
2 x switch/dim actuators, objects for switching, dimming, value setting and value status
must be present.
Group addresses for manual control:
L1 Switch
L2 Switch
L1 Dim
L2 Dim
First put this simple series circuit into operation.
The dimmable lighting in the room should now also be controlled by a brightness control
module dependent on the external light.
Home and Building Management Systems KNX Association
Lighting Control Lighting Control_E0310a.doc 29/34