Page 42 - Advanced Course
P. 42
KNX ADVANCED COURSE
The lowest flow temperature is produced from the required room temperature when the
heating is switched off in the summer. The highest flow temperature is determined by the
type of heating system (low temperature, minimum temperature). In practice, the flow
temperature in the lower range is increased slightly so that there is a temperature
differential between the heater and the room. The following options are available
(depending on the manufacturer) to adapt the heating curve to the conditions and usage
of the building:
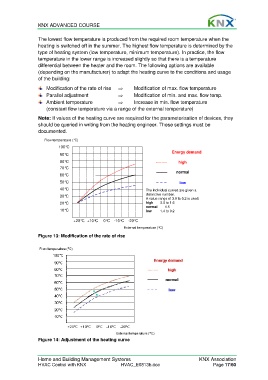
Modification of the rate of rise ⇒ Modification of max. flow temperature
Parallel adjustment ⇒ Modification of min. and max. flow temp.
Ambient temperature ⇒ Increase in min. flow temperature
(constant flow temperature via a range of the external temperature)
Note: If values of the heating curve are required for the parameterisation of devices, they
should be queried in writing from the heating engineer. These settings must be
documented.
Flow temperature (°C)
100°C
Energy demand
90°C
80°C high
70°C
normal
60°C
50°C low
40°C The individual curves are given a
30°C distinctive number.
A value range of 3.0 to 0.2 is used.
20°C high 3.0 to 1.6
normal 1.5
10°C low 1.4 to 0.2
+20°C +10°C 0°C -10°C -20°C
External temperature (°C)
Figure 13: Modification of the rate of rise
Figure 14: Adjustment of the heating curve
Home and Building Management Systems KNX Association
HVAC Control with KNX HVAC_E0813b.doc Page 17/60