Page 121 - Robot Design Handbook ROBOCON Malaysia 2019
P. 121
2.2.2 Electronic Design
The electronic circuit and controller are based on components as listed in Table 1.
The motion of the legs is controlled by the micro-controller and photoelectric sensors [7],
and the modes of operations can be chosen by activating the switches.
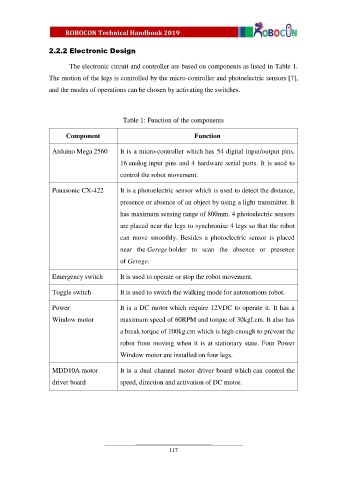
Table 1: Function of the components
Component Function
Arduino Mega 2560 It is a micro-controller which has 54 digital input/output pins,
16 analog input pins and 4 hardware serial ports. It is used to
control the robot movement.
Panasonic CX-422 It is a photoelectric sensor which is used to detect the distance,
presence or absence of an object by using a light transmitter. It
has maximum sensing range of 800mm. 4 photoelectric sensors
are placed near the legs to synchronise 4 legs so that the robot
can move smoothly. Besides a photoelectric sensor is placed
near the Gerege holder to scan the absence or presence
of Gerege.
Emergency switch It is used to operate or stop the robot movement.
Toggle switch It is used to switch the walking mode for autonomous robot.
Power It is a DC motor which require 12VDC to operate it. It has a
Window motor maximum speed of 60RPM and torque of 30kgf.cm. It also has
a break torque of 100kg.cm which is high enough to prevent the
robot from moving when it is at stationary state. Four Power
Window motor are installed on four legs.
MDD10A motor It is a dual channel motor driver board which can control the
driver board speed, direction and activation of DC motor.
117