Page 24 - spectroscopic-atlas-5_0-english_Neat
P. 24
Spectroscopic Atlas for Amateur Astronomers 24
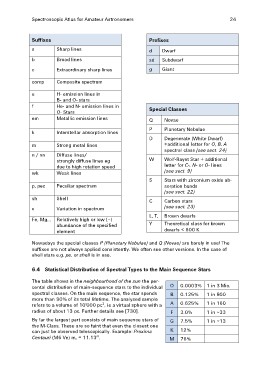
Suffixes Prefixes
s Sharp lines d Dwarf
b Broad lines sd Subdwarf
c Extraordinary sharp lines g Giant
comp Composite spectrum
e H- emission lines in Special Classes
B- and O- stars
Q Novae
f He- and N- emission lines in
O- Stars P Planetary Nebulae
em Metallic emission lines D Degenerate (White Dwarf)
+additional letter for O, B, A
k Interstellar absorption lines spectral class (see sect. 24)
m Strong metal lines W Wolf-Rayet Star + additional
n / nn letter for C-, N- or O- lines
Diffuse lines/ (see sect. 9)
wk strongly diffuse lines eg
due to high rotation speed S Stars with zirconium oxide ab-
Weak lines sorption bands
(see sect. 22)
p, pec Peculiar spectrum
C Carbon stars
sh Shell (see sect. 23)
v Variation in spectrum L, T, Brown dwarfs
Y Theoretical class for brown
Fe, Mg… Relatively high or low (–)
abundance of the specified dwarfs < 600 K
element
Nowadays the special classes P (Planetary Nebulae) and Q (Novae) are barely in use! The
suffixes are not always applied consistently. We often see other versions. In the case of
shell stars e.g. pe, or shell is in use.
6.4 Statistical Distribution of Spectral Types to the Main Sequence Stars
The table shows in the neighbourhood of the sun the per-
cental distribution of main-sequence stars to the individual O 0.0003% 1 in 3 Mio.
spectral classes. On the main sequence, the star spends B 0.125% 1 in 800
A 0.625% 1 in 160
more than 90% of its total lifetime. The analysed sample
refers to a volume of 10'000 pc3, ie a virtual sphere with a
radius of about 13 pc. Further details see [730]. F 3.0% 1 in ~33
By far the largest part consists of main sequence stars of G 7.5% 1 in ~13
K 12%
the M-Class. These are so faint that even the closest one M 76%
can just be observed telescopically. Example: Proxima
Centauri (M6 Ve) mv = 11.13m.