Page 26 - spectroscopic-atlas-5_0-english_Neat
P. 26
Spectroscopic Atlas for Amateur Astronomers 26
8 Spectral Class O
8.1 Overview
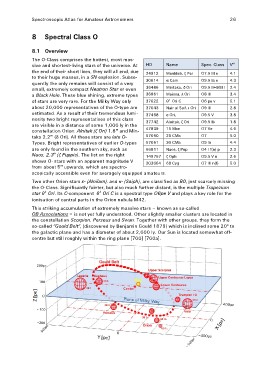
The O-Class comprises the hottest, most mas- Name Spec. Class Vm
sive and shortest-living stars of the universe. At HD
O7.5 III e 4.1
the end of their short lives, they will all end, due 24912 Menkhib, ξ Per O9.5 Ia e 4.3
to their huge masses, in a SN explosion. Subse- 30614 α Cam O9.5 II+B0III 2.4
36486 Mintaka, δ Ori O8 III 3.4
quently the only remains will consist of a very 36861 Meissa, λ Ori O6 pe v 5.1
small, extremely compact Neutron Star or even O9 III 2.8
a Black Hole. These blue shining, extreme types O9.5 V 3.8
O9.5 Ib 1.8
of stars are very rare. For the Milky Way only 37022 Θ1 Ori C O7 Ve 4.6
O7 5.0
about 20,000 representatives of the O-type are 37043 Nair al Saif, ι Ori O9 Ib 4.4
O4 I f(n) p 2.3
estimated. As a result of their tremendous lumi- 37468 σ Ori, O9.5 V n 2.6
37742 Alnitak, ζ Ori O7 III n(f) 5.0
nosity two bright representatives of this class 47839 15 Mon
57060 29 CMa
are visible in a distance of some 1,000 ly in the
constellation Orion: Alnitak (ζ Ori) 1.8m and Min-
taka 2.2m (δ Ori). All these stars are late O-
Types. Bright representatives of earlier O-types 57061 30 CMa
are only found in the southern sky, such as 66811 Naos, ζ Pup
Naos, 2.3m (ζ Puppis). The list on the right 149757 ζ Oph
203064 68 Cyg
shows O- stars with an apparent magnitude V
from about 5m upwards, which are spectro-
scopically accessible even for averagely equipped amateurs.
Two other Orion stars ε- (Alnilam), and κ- (Saiph), are classified as B0, just scarcely missing
the O-Class. Significantly fainter, but also much further distant, is the multiple Trapezium
star θ1 Ori. Its C-component θ1 Ori C is a spectral type O6pe V and plays a key role for the
ionisation of central parts in the Orion nebula M42.
This striking accumulation of extremely massive stars – known as so-called
OB Associations – is not yet fully understood. Other slightly smaller clusters are located in
the constellation Scorpion, Perseus and Swan. Together with other groups, they form the
so-called "Gould Belt", (discovered by Benjamin Gould 1879) which is inclined some 20° to
the galactic plane and has a diameter of about 2,000 ly. Our Sun is located somewhat off-
centre but still roughly within the ring plane [700] [700a].