Page 134 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 134
PLANTS
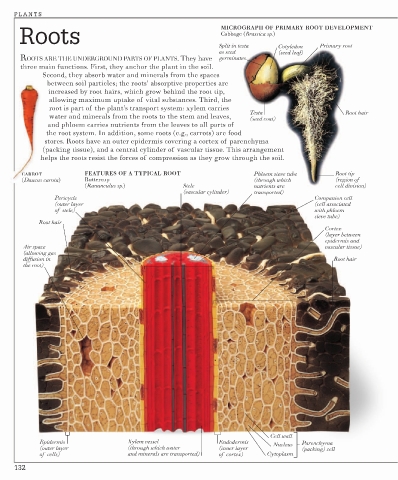
Roots MICROGRAPH OF PRIMARY ROOT DEVELOPMENT
Cabbage (Brassica sp.)
Split in testa Cotyledon Primary root
as seed (seed leaf)
ROOTS ARE THE UNDERGROUND PARTS OF PLANTS. They have germinates
three main functions. First, they anchor the plant in the soil.
Second, they absorb water and minerals from the spaces
between soil particles; the roots’ absorptive properties are
increased by root hairs, which grow behind the root tip,
allowing maximum uptake of vital substances. Third, the
root is part of the plant’s transport system: xylem carries
Testa Root hair
water and minerals from the roots to the stem and leaves,
(seed coat)
and phloem carries nutrients from the leaves to all parts of
the root system. In addition, some roots (e.g., carrots) are food
stores. Roots have an outer epidermis covering a cortex of parenchyma
(packing tissue), and a central cylinder of vascular tissue. This arrangement
helps the roots resist the forces of compression as they grow through the soil.
CARROT FEATURES OF A TYPICAL ROOT Phloem sieve tube Root tip
(Daucus carota) Buttercup (through which (region of
(Ranunculus sp.) Stele nutrients are cell division)
(vascular cylinder) transported)
Pericycle Companion cell
(outer layer (cell associated
of stele) with phloem
sieve tube)
Root hair
Cortex
(layer between
epidermis and
Air space vascular tissue)
(allowing gas
diffusion in Root hair
the root)
Cell wall
Epidermis Xylem vessel Endodermis Nucleus Parenchyma
(outer layer (through which water (inner layer (packing) cell
of cells) and minerals are transported) of cortex) Cytoplasm
132