Page 136 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 136
PLANTS
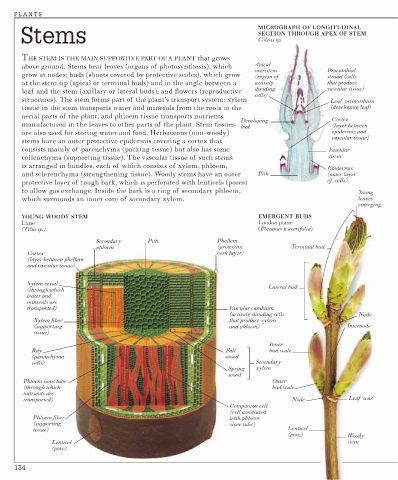
Stems MICROGRAPH OF LONGITUDINAL
SECTION THROUGH APEX OF STEM
Coleus sp.
THE STEM IS THE MAIN SUPPORTIVE PART OF A PLANT that grows
above ground. Stems bear leaves (organs of photosynthesis), which Apical
meristem Procambial
grow at nodes; buds (shoots covered by protective scales), which grow (region of strand (cells
at the stem tip (apical or terminal buds) and in the angle between a actively that produce
leaf and the stem (axillary or lateral buds); and flowers (reproductive dividing vascular tissue)
cells)
structures). The stem forms part of the plant’s transport system: xylem Leaf primordium
tissue in the stem transports water and minerals from the roots to the (developing leaf)
aerial parts of the plant, and phloem tissue transports nutrients
Developing Cortex
manufactured in the leaves to other parts of the plant. Stem tissues bud (layer between
are also used for storing water and food. Herbaceous (non-woody) epidermis and
vascular tissue)
stems have an outer protective epidermis covering a cortex that
consists mainly of parenchyma (packing tissue) but also has some Vascular
collenchyma (supporting tissue). The vascular tissue of such stems tissue
is arranged in bundles, each of which consists of xylem, phloem, Epidermis
and sclerenchyma (strengthening tissue). Woody stems have an outer Pith (outer layer
protective layer of tough bark, which is perforated with lenticels (pores) of cells)
to allow gas exchange. Inside the bark is a ring of secondary phloem, Young
which surrounds an inner core of secondary xylem. leaves
emerging
YOUNG WOODY STEM EMERGENT BUDS
Lime London plane
(Tilia sp.) (Platanus x acerifolia)
Secondary Pith Phellem
phloem (protective Terminal bud
Cortex cork layer)
(layer between phellem
and vascular tissue)
Xylem vessel
(through which Lateral bud
water and
minerals are
transported) Vascular cambium
(actively dividing cells Node
Xylem fiber that produce xylem
(supporting and phloem) Internode
tissue)
Inner
Ray Fall bud scale
(parenchyma wood
cells) Secondary
Spring xylem
wood
Phloem sieve tube Outer
(through which bud scale
nutrients are
transported) Node Leaf scar
Companion cell
(cell associated
Phloem fiber with phloem
(supporting sieve tube)
tissue) Lenticel
(pore) Woody
Lenticel stem
(pore)
134