Page 140 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 140
PLANTS
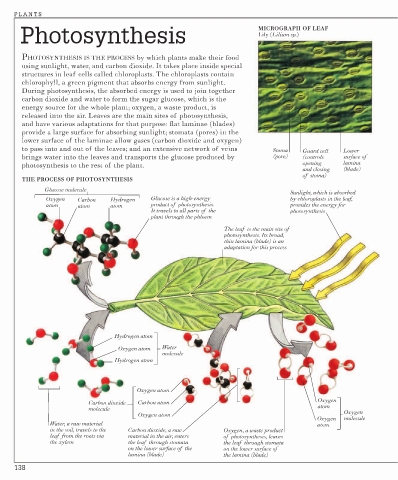
Photosynthesis MICROGRAPH OF LEAF
Lily (Lilium sp.)
PHOTOSYNTHESIS IS THE PROCESS by which plants make their food
using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. It takes place inside special
structures in leaf cells called chloroplasts. The chloroplasts contain
chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs energy from sunlight.
During photosynthesis, the absorbed energy is used to join together
carbon dioxide and water to form the sugar glucose, which is the
energy source for the whole plant; oxygen, a waste product, is
released into the air. Leaves are the main sites of photosynthesis,
and have various adaptations for that purpose: flat laminae (blades)
provide a large surface for absorbing sunlight; stomata (pores) in the
lower surface of the laminae allow gases (carbon dioxide and oxygen)
to pass into and out of the leaves; and an extensive network of veins Stoma Guard cell Lower
brings water into the leaves and transports the glucose produced by (pore) (controls surface of
photosynthesis to the rest of the plant. opening lamina
and closing (blade)
of stoma)
THE PROCESS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Glucose molecule
Sunlight, which is absorbed
Oxygen Carbon Hydrogen Glucose is a high-energy by chloroplasts in the leaf,
atom atom atom product of photosynthesis. provides the energy for
It travels to all parts of the photosynthesis
plant through the phloem
The leaf is the main site of
photosynthesis. Its broad,
thin lamina (blade) is an
adaptation for this process
Hydrogen atom
Oxygen atom Water
molecule
Hydrogen atom
Oxygen atom
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide Carbon atom
atom
molecule Oxygen
Oxygen atom
Oxygen molecule
Water, a raw material atom
in the soil, travels to the Carbon dioxide, a raw Oxygen, a waste product
leaf from the roots via material in the air, enters of photosynthesis, leaves
the xylem the leaf through stomata the leaf through stomata
on the lower surface of the on the lower surface of
lamina (blade) the lamina (blade)
138