Page 148 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 148
PLANTS
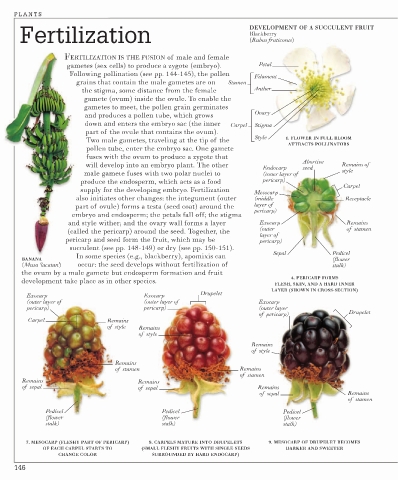
Fertilization DEVELOPMENT OF A SUCCULENT FRUIT
Blackberry
(Rubus fruticosus)
FERTILIZATION IS THE FUSION of male and female
gametes (sex cells) to produce a zygote (embryo). Petal
Following pollination (see pp. 144-145), the pollen
Filament
grains that contain the male gametes are on Stamen
the stigma, some distance from the female Anther
gamete (ovum) inside the ovule. To enable the
gametes to meet, the pollen grain germinates
and produces a pollen tube, which grows Ovary
down and enters the embryo sac (the inner Carpel Stigma
part of the ovule that contains the ovum).
Style 1. FLOWER IN FULL BLOOM
Two male gametes, traveling at the tip of the
ATTRACTS POLLINATORS
pollen tube, enter the embryo sac. One gamete
fuses with the ovum to produce a zygote that
Abortive
will develop into an embryo plant. The other Remains of
Endocarp seed
male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei to (inner layer of style
produce the endosperm, which acts as a food pericarp)
Carpel
supply for the developing embryo. Fertilization
Mesocarp
also initiates other changes: the integument (outer (middle Receptacle
part of ovule) forms a testa (seed coat) around the layer of
pericarp)
embryo and endosperm; the petals fall off; the stigma
and style wither; and the ovary wall forms a layer Exocarp Remains
(called the pericarp) around the seed. Together, the (outer of stamen
layer of
pericarp and seed form the fruit, which may be pericarp)
succulent (see pp. 148-149) or dry (see pp. 150-151).
Sepal Pedicel
In some species (e.g., blackberry), apomixis can
BANANA (flower
(Musa ‘lacatan’) occur: the seed develops without fertilization of stalk)
the ovum by a male gamete but endosperm formation and fruit
4. PERICARP FORMS
development take place as in other species.
FLESH, SKIN, AND A HARD INNER
LAYER (SHOWN IN CROSS-SECTION)
Drupelet
Exocarp Exocarp
(outer layer of (outer layer of Exocarp
pericarp) pericarp) (outer layer
of pericarp) Drupelet
Carpel Remains
of style Remains
of style
Remains
of style
Remains
of stamen Remains
of stamen
Remains Remains
of sepal of sepal Remains
of sepal Remains
of stamen
Pedicel Pedicel Pedicel
(flower (flower (flower
stalk) stalk) stalk)
7. MESOCARP (FLESHY PART OF PERICARP) 8. CARPELS MATURE INTO DRUPELETS 9. MESOCARP OF DRUPELET BECOMES
OF EACH CARPEL STARTS TO (SMALL FLESHY FRUITS WITH SINGLE SEEDS DARKER AND SWEETER
CHANGE COLOR SURROUNDED BY HARD ENDOCARP)
146