Page 154 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 154
PLANTS
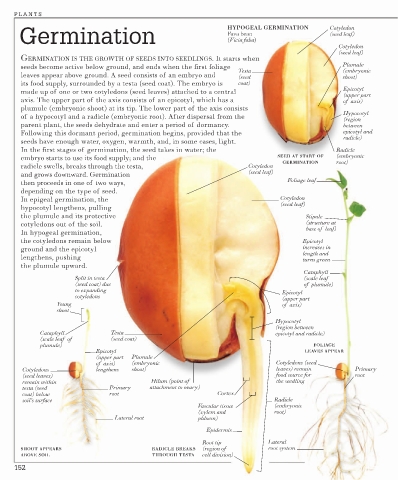
Germination HYPOGEAL GERMINATION Cotyledon
(seed leaf)
Fava bean
(Vicia faba)
Cotyledon
(seed leaf)
GERMINATION IS THE GROWTH OF SEEDS INTO SEEDLINGS. It starts when
seeds become active below ground, and ends when the first foliage Plumule
Testa (embryonic
leaves appear above ground. A seed consists of an embryo and (seed shoot)
its food supply, surrounded by a testa (seed coat). The embryo is coat)
Epicotyl
made up of one or two cotyledons (seed leaves) attached to a central
(upper part
axis. The upper part of the axis consists of an epicotyl, which has a of axis)
plumule (embryonic shoot) at its tip. The lower part of the axis consists
Hypocotyl
of a hypocotyl and a radicle (embryonic root). After dispersal from the
(region
parent plant, the seeds dehydrate and enter a period of dormancy. between
Following this dormant period, germination begins, provided that the epicotyl and
radicle)
seeds have enough water, oxygen, warmth, and, in some cases, light.
In the first stages of germination, the seed takes in water; the Radicle
embryo starts to use its food supply; and the SEED AT START OF (embryonic
GERMINATION root)
radicle swells, breaks through the testa, Cotyledon
(seed leaf)
and grows downward. Germination
Foliage leaf
then proceeds in one of two ways,
depending on the type of seed.
In epigeal germination, the Cotyledon
(seed leaf)
hypocotyl lengthens, pulling
the plumule and its protective Stipule
cotyledons out of the soil. (structure at
base of leaf)
In hypogeal germination,
the cotyledons remain below Epicotyl
ground and the epicotyl increases in
length and
lengthens, pushing turns green
the plumule upward.
Cataphyll
Split in testa (scale leaf
(seed coat) due of plumule)
to expanding Epicotyl
cotyledons
(upper part
Young of axis)
shoot
Hypocotyl
(region between
Cataphyll Testa epicotyl and radicle)
(scale leaf of (seed coat)
plumule) FOLIAGE
Epicotyl LEAVES APPEAR
(upper part Plumule
of axis) (embryonic Cotyledons (seed
Cotyledons lengthens shoot) leaves) remain Primary
(seed leaves) food source for root
remain within Hilum (point of the seedling
testa (seed Primary attachment to ovary)
coat) below root Cortex
soil’s surface Radicle
Vascular tissue (embryonic
(xylem and root)
Lateral root phloem)
Epidermis
Root tip Lateral
SHOOT APPEARS RADICLE BREAKS (region of root system
ABOVE SOIL THROUGH TESTA cell division)
152