Page 64 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 64
PREHISTORIC EAR TH
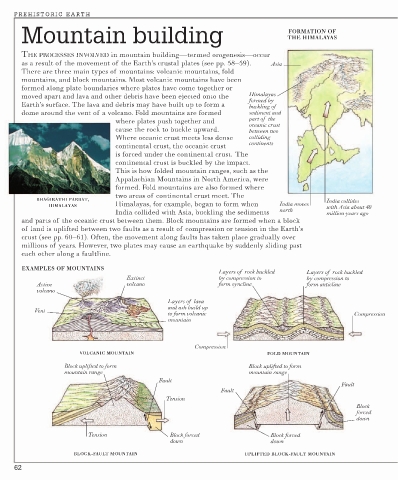
Mountain building THE HIMALAYAS
FORMATION OF
THE PROCESSES INVOLVED in mountain building—termed orogenesis—occur
as a result of the movement of the Earth’s crustal plates (see pp. 58–59). Asia
There are three main types of mountains: volcanic mountains, fold
mountains, and block mountains. Most volcanic mountains have been
formed along plate boundaries where plates have come together or
moved apart and lava and other debris have been ejected onto the Himalayas
formed by
Earth’s surface. The lava and debris may have built up to form a buckling of
dome around the vent of a volcano. Fold mountains are formed sediment and
part of the
where plates push together and
oceanic crust
cause the rock to buckle upward. between two
Where oceanic crust meets less dense colliding
continents
continental crust, the oceanic crust
is forced under the continental crust. The
continental crust is buckled by the impact.
This is how folded mountain ranges, such as the
Appalachian Mountains in North America, were
formed. Fold mountains are also formed where
two areas of continental crust meet. The
BHAGIRATHI PARBAT, India collides
HIMALAYAS Himalayas, for example, began to form when India moves with Asia about 40
India collided with Asia, buckling the sediments north million years ago
and parts of the oceanic crust between them. Block mountains are formed when a block
of land is uplifted between two faults as a result of compression or tension in the Earth’s
crust (see pp. 60–61). Often, the movement along faults has taken place gradually over
millions of years. However, two plates may cause an earthquake by suddenly sliding past
each other along a faultline.
EXAMPLES OF MOUNTAINS
Layers of rock buckled Layers of rock buckled
Extinct by compression to by compression to
Active volcano form syncline form anticline
volcano
Layers of lava
and ash build up
Vent
to form volcanic Compression
mountain
Compression
VOLCANIC MOUNTAIN FOLD MOUNTAIN
Block uplifted to form Block uplifted to form
mountain range mountain range
Fault
Fault
Fault
Tension
Block
forced
down
Tension Block forced Block forced
down down
BLOCK-FAULT MOUNTAIN UPLIFTED BLOCK-FAULT MOUNTAIN
62