Page 65 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 65
MOUNTAIN BUILDING
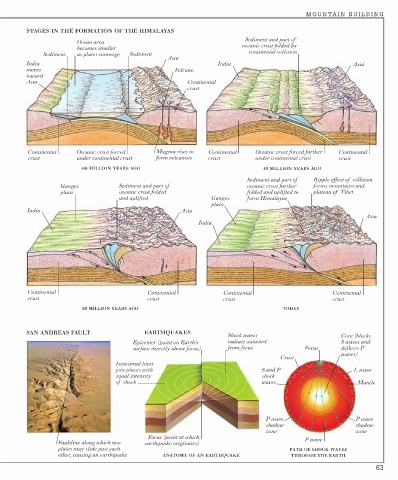
STAGES IN THE FORMATION OF THE HIMALAYAS
Sediment and part of
Ocean area
becomes smaller oceanic crust folded by
Sediment as plates converge Sediment continental collision
Asia
India India Asia
moves Volcano
toward
Asia Continental
crust
Continental Oceanic crust forced Magma rises to Continental Oceanic crust forced farther Continental
crust under continental crust form volcanoes crust under continental crust crust
60 MILLION YEARS AGO 40 MILLION YEARS AGO
Sediment and part of Ripple effect of collision
Ganges Sediment and part of oceanic crust farther forms mountains and
plain oceanic crust folded folded and uplifted to plateau of Tibet
and uplifted Ganges form Himalayas
plain
India Asia
Asia
India
Continental Continental Continental Continental
crust crust crust crust
20 MILLION YEARS AGO TODAY
SAN ANDREAS FAULT EARTHQUAKES
Shock waves Core (blocks
Epicenter (point on Earth’s radiate outward S waves and
surface directly above focus) from focus Focus deflects P
waves)
Crust
Isoseismal lines
join places with S and P L wave
equal intensity shock
of shock waves Mantle
P wave P wave
shadow shadow
zone zone
Focus (point at which P wave
Faultline along which two earthquake originates)
plates may slide past each PATH OF SHOCK WAVES
other, causing an earthquake ANATOMY OF AN EARTHQUAKE THROUGH THE EARTH
63