Page 36 - (DK Eyewitness) Travel Guide - Europe
P. 36
34 EUROPE A T A GLANCE
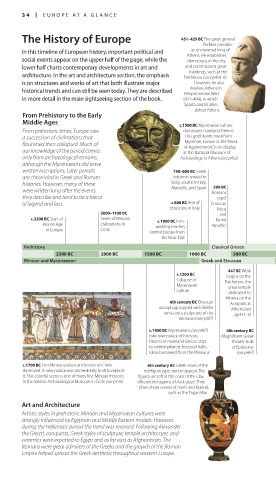
The History of Europe 451–429 BC The great general
Perikles presides
as uncrowned king of
In this timeline of European history, important political and Athens. He establishes
social events appear on the upper half of the page, while the democracy in the city
lower half charts contemporary developments in art and and commissions great
buildings, such as the
architecture. In the art and architecture section, the emphasis Parthenon (see pp454–6).
is on structures and works of art that both illustrate major However, he also
involves Athens in
historical trends and can still be seen today. They are described Peloponnesian Wars
in more detail in the main sightseeing section of the book. (431–404), in which
Sparta and its allies
defeat Athens
From Prehistory to the Early
Middle Ages
c.1500 BC Mycenaean culture
From prehistoric times, Europe saw dominates mainland Greece.
a succession of civilizations that This gold death mask from
Mycenae, known as the “Mask
flourished then collapsed. Much of of Agamemnon,” is on display
our knowledge of the period comes at the National Museum of
only from archaeological remains, Archaeology in Athens (see p452)
although the Mycenaeans did leave
written inscriptions. Later periods 750–600 BC Greek
are chronicled in Greek and Roman colonists spread to
histories. However, many of these Sicily, southern Italy, 509 BC
were written long after the events Marseille, and Spain Romans
they describe and tend to be a blend expel
of legend and fact. c.800 BC Rise of Etruscan
Etruscans in Italy kings
2000–1100 BC and
c.2300 BC Start of Series of Minoan c.1000 BC Iron- found
Bronze Age civilizations in working reaches republic
in Europe Crete
central Europe from
the Near East
Prehistory Classical Greece
2500 BC 2000 BC 1500 BC 1000 BC 500 BC
Minoan and Mycenanean Greek and Etruscan Hellenistic and Roman
447 BC Work
c.1200 BC begins on the
Collapse of Parthenon, the
Mycenaean great temple
culture
dedicated to
Athena on the
6th century BC Etruscan Acropolis in
sarcophagi topped with lifelike Athens (see
terra-cotta sculptures of the pp454–6)
deceased (see p387)
c.1450 BC Mycenaeans (see p467) 4th century BC
take over palace of Knossos. Magnificent Greek
Palaces in mainland Greece start theater built
to exhibit pillared, frescoed halls; at Epidaurus
ideas borrowed from the Minoans (see p467)
c.1700 BC First Minoan palace at Knossos on Crete 6th century BC Greek vases of the
destroyed. A new palace was immediately built to replace red-figure type start to appear. The
it. This colorful scene is one of many fine Minoan frescoes figures are left in the color of the clay,
in the Irákleio Archaeological Museum in Crete (see p476) silhouetted against a black glaze. They
often show scenes of myth and legend,
such as the Trojan War
Art and Architecture
Artistic styles in prehistoric Minoan and Mycenaean cultures were
strongly influenced by Egyptian and Middle Eastern models. However,
during the Hellenistic period the trend was reversed. Following Alexander
the Great’s conquests, Greek styles of sculpture, temple architecture, and
ceramics were exported to Egypt and as far east as Afghanistan. The
Romans were great admirers of the Greeks and the growth of the Roman
Empire helped spread the Greek aesthetic throughout western Europe.
034-035_EW_Europe.indd 34 14/07/16 10:44 am