Page 158 - Nilam_Publication_module_Chemistry_Form.pdf
P. 158
MODULE • Chemistry Form 4
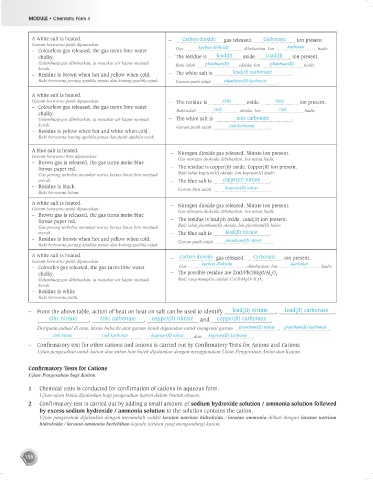
A white salt is heated. – Carbon dioxide gas released. Carbonate ion present
Garam berwarna putih dipanaskan. karbonat
– Colourless gas released, the gas turns lime water Gas karbon dioksida dibebaskan. Ion hadir.
chalky. – The residue is lead(II) oxide. Lead(II) ion present.
Gelembung gas dibebaskan, ia menukar air kapur menjadi Baki ialah plumbum(II) oksida. Ion plumbum(II) hadir.
keruh.
– Residue is brown when hot and yellow when cold. – The white salt is lead(II) carbonate .
Baki berwarna perang apabila panas dan kuning apabila sejuk. Garam putih ialah plumbum(II) karbonat .
A white salt is heated.
Garam berwarna putih dipanaskan. – The residue is zinc oxide. zinc ion present.
– Colourless gas released, the gas turns lime water zink zink
chalky. Baki ialah oksida. Ion hadir.
Gelembung gas dibebaskan, ia menukar air kapur menjadi – The white salt is zinc carbonate .
keruh. Garam putih ialah zink karbonat .
– Residue is yellow when hot and white when cold.
Baki berwarna kuning apabila panas dan putih apabila sejuk.
A blue salt is heated. – Nitrogen dioxide gas released. Nitrate ion present.
Garam berwarna biru dipanaskan. Gas nitrogen dioksida dibebaskan. Ion nitrat hadir.
– Brown gas is released, the gas turns moist blue
litmus paper red. – The residue is copper(II) oxide. Copper(II) ion present.
Gas perang terbebas menukar warna kertas limus biru menjadi Baki ialah kuprum(II) oksida. Ion kuprum(II) hadir.
merah. – The blue salt is copper(II) nitrate .
– Residue is black. kuprum(II) nitrat
Baki berwarna hitam. Garam biru ialah .
A white salt is heated. – Nitrogen dioxide gas released. Nitrate ion present.
Garam berwarna putih dipanaskan. Gas nitrogen dioksida dibebaskan. Ion nitrat hadir.
– Brown gas is released, the gas turns moist blue
litmus paper red. – The residue is lead(II) oxide. Lead(II) ion present.
Gas perang terbebas menukar warna kertas limus biru menjadi Baki ialah plumbum(II) oksida. Ion plumbum(II) hadir.
merah. – The blue salt is lead(II) nitrate .
– Residue is brown when hot and yellow when cold. plumbum(II) nitrat
Baki berwarna perang apabila panas dan kuning apabila sejuk. Garam putih ialah .
A white salt is heated. – Carbon dioxide gas released. Carbonate ion present.
Garam berwarna putih dipanaskan. karbon dioksida karbonat
– Colourles gas released, the gas turns lime water Gas dibebaskan. Ion hadir.
chalky. – The possible residue are ZnO/PbO/MgO/Al O
3
2
Gelembung gas dibebaskan, ia menukar air kapur menjadi Baki yang mungkin adalah CaOl/MgO/Al O .
3
2
keruh.
– Residue is white
Baki berwarna putih.
– From the above table, action of heat on heat on salt can be used to identify lead(II) nitrate , lead(II) carbonate ,
zinc nitrate , zinc carbonate , copper(II) nitrate and copper(II) carbonate .
Daripada jadual di atas, kesan haba ke atas garam boleh digunakan untuk mengenal garam plumbum(II) nitrat , plumbum(II) karbonat ,
zink nitrat , zink karbonat , kuprum(II) nitrat dan kuprum(II) karbonat .
– Confirmatory test for other cations and anions is carried out by Confirmatory Tests for Anions and Cations
Ujian pengesahan untuk kation dan anion lain boleh dijalankan dengan menggunakan Ujian Pengesahan Anion dan Kation.
Conf rmatory Tests for Cations
Ujian Pengesahan bagi Kation
1 Chemical tests is conducted for confirmation of cations in aqueous form.
Ujian-ujian kimia dijalankan bagi pengesahan kation dalam bentuk akueus.
2 Confirmatory test is carried out by adding a small amount of sodium hydroxide solution / ammonia solution followed
by excess sodium hydroxide / ammonia solution to the solution contains the cation.
Ujian pengesahan dijalankan dengan menambah sedikit larutan natrium hidroksida / larutan ammonia diikuti dengan larutan natrium
hidroksida / larutan ammonia berlebihan kepada larutan yang mengandungi kation.
156
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
07-Chem F4 (3p).indd 156 12/9/2011 5:55:23 PM