Page 210 - เอกสารประกอบการอบรม คณิตศาสตร์
P. 210
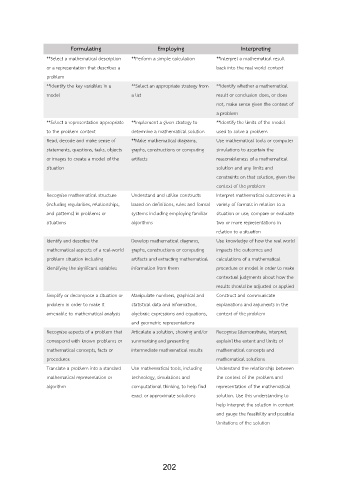
Formulating Employing Interpreting
**Select a mathematical description **Perform a simple calculation **Interpret a mathematical result
or a representation that describes a back into the real world context
problem
**Identify the key variables in a **Select an appropriate strategy from **Identify whether a mathematical
model a list result or conclusion does, or does
not, make sense given the context of
a problem
**Select a representation appropriate **Implement a given strategy to **Identify the limits of the model
to the problem context determine a mathematical solution used to solve a problem
Read, decode and make sense of **Make mathematical diagrams, Use mathematical tools or computer
statements, questions, tasks, objects graphs, constructions or computing simulations to ascertain the
or images to create a model of the artifacts reasonableness of a mathematical
situation solution and any limits and
constraints on that solution, given the
context of the problem
Recognise mathematical structure Understand and utilise constructs Interpret mathematical outcomes in a
(including regularities, relationships, based on definitions, rules and formal variety of formats in relation to a
and patterns) in problems or systems including employing familiar situation or use; compare or evaluate
situations algorithms two or more representations in
relation to a situation
Identify and describe the Develop mathematical diagrams, Use knowledge of how the real world
mathematical aspects of a real-world graphs, constructions or computing impacts the outcomes and
problem situation including artifacts and extracting mathematical calculations of a mathematical
identifying the significant variables information from them procedure or model in order to make
contextual judgments about how the
results should be adjusted or applied
Simplify or decompose a situation or Manipulate numbers, graphical and Construct and communicate
problem in order to make it statistical data and information, explanations and arguments in the
amenable to mathematical analysis algebraic expressions and equations, context of the problem
and geometric representations
Recognise aspects of a problem that Articulate a solution, showing and/or Recognise [demonstrate, interpret,
correspond with known problems or summarising and presenting explain] the extent and limits of
mathematical concepts, facts or intermediate mathematical results mathematical concepts and
procedures mathematical solutions
Translate a problem into a standard Use mathematical tools, including Understand the relationship between
mathematical representation or technology, simulations and the context of the problem and
algorithm computational thinking, to help find representation of the mathematical
exact or approximate solutions solution. Use this understanding to
help interpret the solution in context
and gauge the feasibility and possible
limitations of the solution
202