Page 110 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 110
66 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—NUTRITION BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—NUTRITION
Vitamin A Includes retinal, retinol, retinoic acid.
FUNCTION Antioxidant; constituent of visual pigments Retinol is vitamin A, so think retin-A (used
(retinal); essential for normal differentiation topically for wrinkles and Acne).
of epithelial cells into specialized tissue Found in liver and leafy vegetables.
(pancreatic cells, mucus-secreting cells); Supplementation in vitamin A-deficient measles
prevents squamous metaplasia. Used to treat patients may improve outcomes.
measles and acute promyelocytic leukemia Use oral isotretinoin to treat severe cystic acne.
(APL). Use all-trans retinoic acid to treat acute
promyelocytic leukemia.
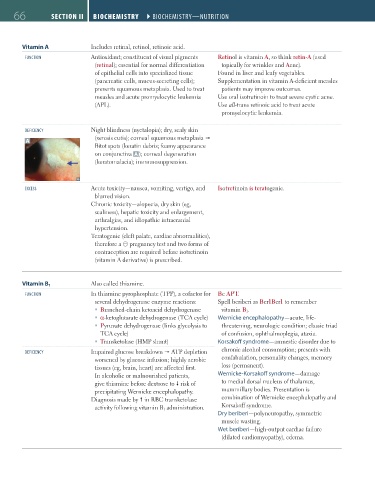
DEFICIENCY Night blindness (nyctalopia); dry, scaly skin
(xerosis cutis); corneal squamous metaplasia
A
Bitot spots (keratin debris; foamy appearance
on conjunctiva A ); corneal degeneration
(keratomalacia); immunosuppression.
EXCESS Acute toxicity—nausea, vomiting, vertigo, and Isotretinoin is teratogenic.
blurred vision.
Chronic toxicity—alopecia, dry skin (eg,
scaliness), hepatic toxicity and enlargement,
arthralgias, and idiopathic intracranial
hypertension.
Teratogenic (cleft palate, cardiac abnormalities),
therefore a ⊝ pregnancy test and two forms of
contraception are required before isotretinoin
(vitamin A derivative) is prescribed.
Vitamin B 1 Also called thiamine.
FUNCTION In thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), a cofactor for Be APT.
several dehydrogenase enzyme reactions: Spell beriberi as Ber1Ber1 to remember
Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase vitamin B 1 .
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (TCA cycle) Wernicke encephalopathy—acute, life-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (links glycolysis to threatening, neurologic condition; classic triad
TCA cycle) of confusion, ophthalmoplegia, ataxia.
Transketolase (HMP shunt) Korsakoff syndrome—amnestic disorder due to
DEFICIENCY Impaired glucose breakdown ATP depletion chronic alcohol consumption; presents with
worsened by glucose infusion; highly aerobic confabulation, personality changes, memory
tissues (eg, brain, heart) are affected first. loss (permanent).
In alcoholic or malnourished patients, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome—damage
give thiamine before dextrose to risk of to medial dorsal nucleus of thalamus,
precipitating Wernicke encephalopathy. mammillary bodies. Presentation is
Diagnosis made by in RBC transketolase combination of Wernicke encephalopathy and
activity following vitamin B 1 administration. Korsakoff syndrome.
Dry beriberi—polyneuropathy, symmetric
muscle wasting.
Wet beriberi—high-output cardiac failure
(dilated cardiomyopathy), edema.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 66 11/7/19 3:16 PM