Page 105 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 105
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS SECTION II 61
X-linked recessive Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, Fabry Oblivious Female Will Often Give Her Boys
disorders disease, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Ocular Her x-Linked Disorders
albinism, G6PD deficiency, Hunter syndrome,
Bruton agammaglobulinemia, Hemophilia
A and B, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, Duchenne
(and Becker) muscular dystrophy.
X-inactivation (lyonization)—one copy Females with Turner syndrome (45,XO) are
of female X chromosome forms a more likely to have an X-linked recessive
transcriptionally inactive Barr body. Female disorder.
carriers variably affected depending on the
pattern of inactivation of the X chromosome
carrying the mutant vs normal gene.
Muscular dystrophies
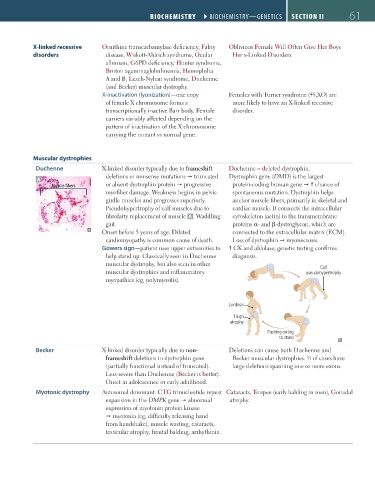
Duchenne X-linked disorder typically due to frameshift Duchenne = deleted dystrophin.
A deletions or nonsense mutations truncated Dystrophin gene (DMD) is the largest
Muscle fibers or absent dystrophin protein progressive protein-coding human gene chance of
myofiber damage. Weakness begins in pelvic spontaneous mutation. Dystrophin helps
girdle muscles and progresses superiorly. anchor muscle fibers, primarily in skeletal and
Pseudohypertrophy of calf muscles due to cardiac muscle. It connects the intracellular
fibrofatty replacement of muscle A . Waddling cytoskeleton (actin) to the transmembrane
gait. proteins α- and β-dystroglycan, which are
Onset before 5 years of age. Dilated connected to the extracellular matrix (ECM).
cardiomyopathy is common cause of death. Loss of dystrophin myonecrosis.
Gowers sign—patient uses upper extremities to CK and aldolase; genetic testing confirms
help stand up. Classically seen in Duchenne diagnosis.
muscular dystrophy, but also seen in other Calf
muscular dystrophies and inflammatory pseudohypertrophy
myopathies (eg, polymyositis).
Lordosis
Thigh
atrophy
Pushing on leg
to stand
Becker X-linked disorder typically due to non- Deletions can cause both Duchenne and
frameshift deletions in dystrophin gene Becker muscular dystrophies. ⁄3 of cases have
2
(partially functional instead of truncated). large deletions spanning one or more exons.
Less severe than Duchenne (Becker is better).
Onset in adolescence or early adulthood.
Myotonic dystrophy Autosomal dominant. CTG trinucleotide repeat Cataracts, Toupee (early balding in men), Gonadal
expansion in the DMPK gene abnormal atrophy.
expression of myotonin protein kinase
myotonia (eg, difficulty releasing hand
from handshake), muscle wasting, cataracts,
testicular atrophy, frontal balding, arrhythmia.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 61 11/7/19 3:16 PM