Page 106 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 106
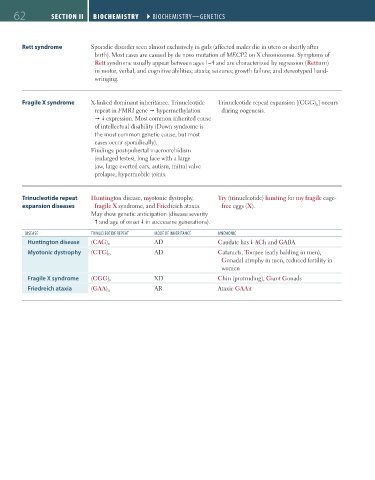
62 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS
Rett syndrome Sporadic disorder seen almost exclusively in girls (affected males die in utero or shortly after
birth). Most cases are caused by de novo mutation of MECP2 on X chromosome. Symptoms of
Rett syndrome usually appear between ages 1–4 and are characterized by regression (Retturn)
in motor, verbal, and cognitive abilities; ataxia; seizures; growth failure; and stereotyped hand-
wringing.
Fragile X syndrome X-linked dominant inheritance. Trinucleotide Trinucleotide repeat expansion [(CGG) n ] occurs
repeat in FMR1 gene hypermethylation during oogenesis.
expression. Most common inherited cause
of intellectual disability (Down syndrome is
the most common genetic cause, but most
cases occur sporadically).
Findings: post-pubertal macroorchidism
(enlarged testes), long face with a large
jaw, large everted ears, autism, mitral valve
prolapse, hypermobile joints.
Trinucleotide repeat Huntington disease, myotonic dystrophy, Try (trinucleotide) hunting for my fragile cage-
expansion diseases fragile X syndrome, and Friedreich ataxia. free eggs (X).
May show genetic anticipation (disease severity
and age of onset in successive generations).
DISEASE TRINUClEOTIDE REPEAT MODE OF INHERITANCE MNEMONIC
Huntington disease (CAG) n AD Caudate has ACh and GABA
Myotonic dystrophy (CTG) n AD Cataracts, Toupee (early balding in men),
Gonadal atrophy in men, reduced fertility in
women
Fragile X syndrome (CGG) n XD Chin (protruding), Giant Gonads
Friedreich ataxia (GAA) n AR Ataxic GAAit
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 62 11/7/19 3:16 PM